Vitamin D

Vitamin D
Vitamin D helps regulate the amount of calcium and phosphate in the body.
These nutrients are needed to keep bones, teeth, and muscles healthy.
A lack of vitamin D can lead to bone deformities such as rickets in children and bone pain caused by a condition called osteomalacia in adults.
Government advice is that everyone should consider taking a daily vitamin D supplement during the autumn and winter.
People at high risk of not getting enough vitamin D, all children aged 1 to 4, and all babies (unless they’re having more than 500ml of infant formula a day) should take a daily supplement throughout the year.
Good sources of vitamin D
From about late March/early April to the end of September, most people should be able to make all the vitamin D they need from sunlight.
The body creates vitamin D from direct sunlight on the skin when outdoors.
But we do not make enough vitamin D from sunlight between October and early March. Read more about vitamin D and sunlight.
Vitamin D is also found in a small number of foods.
Sources include:
- oily fish – such as salmon, sardines, herring, and mackerel
- red meat
- liver
- egg yolks
- fortified foods – such as some fat spreads and breakfast cereals
Another source of vitamin D is dietary supplements.
In the UK, cows’ milk is generally not a good source of vitamin D because it is not fortified as in some other countries.
How much vitamin D do I need?
- From about late March/early April to the end of September, most people should be able to make all the vitamin D they need from sunlight on their skin.
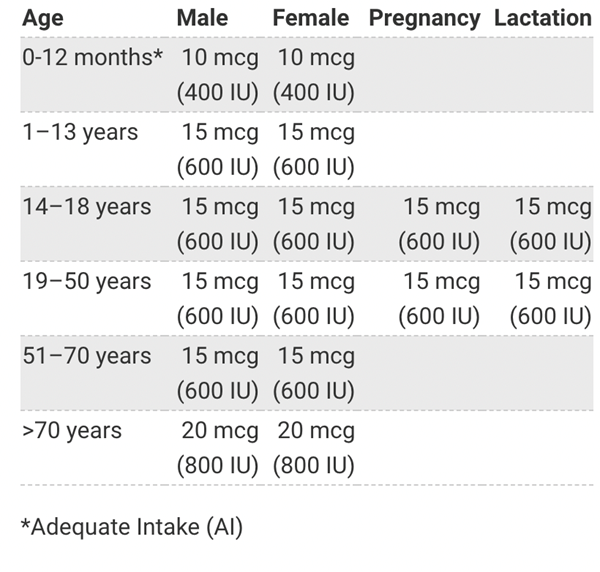
- Children from the age of 1 year and adults need 10ten micrograms of vitamin D daily. This includes pregnant and breastfeeding women and people at risk of vitamin D deficiency.
- Babies up to the age of 1 year need 8.5 to 10 micrograms of vitamin D a day.
- A microgram is 1,000 times smaller than a milligram (mg). The word microgram is sometimes written with the Greek symbol μ followed by the letter g (μg).
- Sometimes the amount of vitamin D is expressed as International Units (IU). 1One microgram of vitamin D is equal to 40 IU. So 10ten micrograms of vitamin D is equivalent to 400 IU.
Should I take a vitamin D supplement?
- Advice for adults and children over four years old
- During the autumn and winter, you need to get vitamin D from your diet because the sun is not strong enough for the body to make vitamin D.
- But since it’s difficult for people to get enough vitamin D from food alone, everyone (including pregnant and breastfeeding women) should consider taking a daily supplement containing ten micrograms of vitamin D during the autumn and winter.
- Between late March/early April to the end of September, most people can make all the vitamin D they need through sunlight on their skin and from a balanced diet.
- You may choose not to take a vitamin D supplement during these months.
People at risk of vitamin D deficiency
- Some people will not make enough vitamin D from sunlight because they have little or no sunshine exposure.
- The Department of Health and Social Care recommends that adults and children over 4 take a daily supplement containing ten micrograms of vitamin D throughout the year if they:
- are not often outdoors – for example, if they’re frail or housebound
- are in an institution like a care home
- usually wear clothes that cover up most of their skin when outdoors
- If you have dark skin – for example , an African, African-Caribbean or south Asian background – you may also not make enough from sunlight.
- It would help if you considered taking a daily supplement containing ten micrograms of throughout the year.
Advice for infants and young children
- The Department of Health and Social Care recommends that babies from birth to 1 year of age should have a daily supplement containing 8.5 to 10 micrograms of vitamin D throughout the year if they are:
- breastfed
- Formula-fed and have less than 500ml (about a pint) of infant formula daily, as infant formula is already fortified with vitamin D.
- Children aged 1 to 4 should be given a daily supplement containing ten micrograms of vitamin D throughout the year.
- You can buy its supplements or drops containing vitamin D (for under 5s) at most pharmacies and supermarkets.
- Women and children who qualify for the Healthy Start scheme can get free supplements containing it.
- See the Healthy Start website for more information.
Recommended Intakes
- Intake recommendations for vitamin D and other nutrients are provided in the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) developed by expert committees of NASEM.
- DRI is the general term for a set of reference values used for planning and assessing nutrient intakes of healthy people. These values, which vary by age and sex, include:
- Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA): Average daily level of intake sufficient to meet the nutrient requirements of nearly all (97%–98%) healthy individuals; often used to plan nutritionally adequate diets for individuals.
- Adequate Intake (AI): Intake at this level is assumed to ensure nutritional adequacy; established when evidence is insufficient to develop an RDA.
- Estimated Average Requirement (EAR): Average daily level of intake estimated to meet the requirements of 50% of healthy individuals; usually used to assess the nutrient intakes of groups of people and to plan nutritionally adequate diets for them; can also be used to assess the nutrient intakes of individuals.
- Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL): Maximum daily intake unlikely to cause adverse health effects.
- An FNB committee established RDAs for it to indicate daily intakes sufficient to maintain bone health and normal calcium metabolism in healthy people.
Benefits of vitamin D2 vs benefits of D3
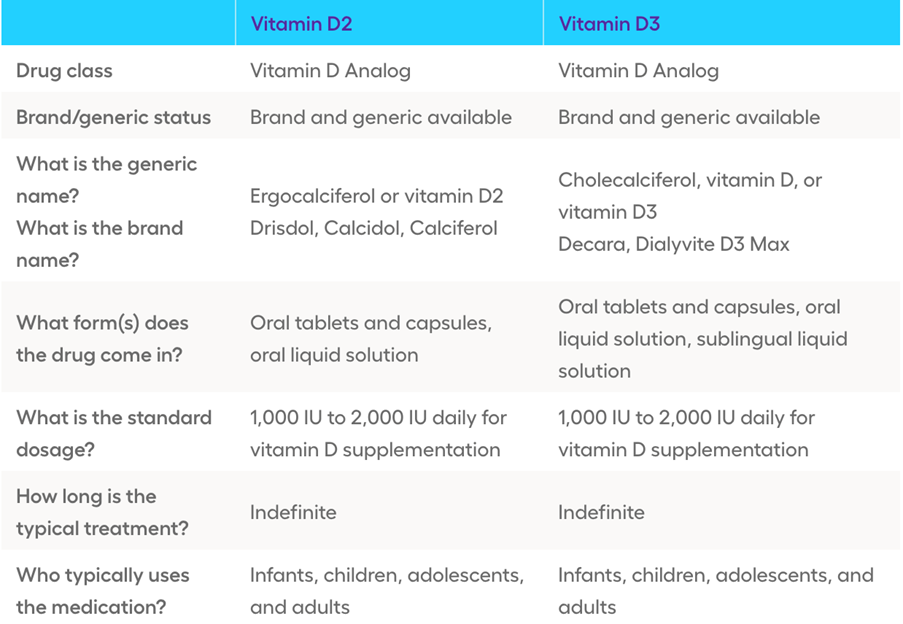
- Vitamin D2 and vitamin D3 are the two main forms of it.
- Scientists sometimes call D2 ergocalciferol and D3 cholecalciferol Trusted Source.
- Both play the same role in the body, but vitamins D2 and D3 have slightly different molecular structures. The main difference is that vitamin D2 comes from plants, whereas D3 comes from animals, including people.
- Scientists are not sure yet if one is better than the other for human health.
- According to the National Institute of Health’s Office of Dietary Supplements, both types will increase the levels of in a person’s blood.
- Vitamin D3 may raise levels higher and for longer than D2. A 2012 review indicates that vitamin D3 appeared to be better at raising vitamin D levels than D2.
- However, the review also said researchers needed more evidence before they could be sure how the two types affected different groups of people, such as people of different ages, sexes, and ethnicities. In addition, the study looked at vitamin D supplements, not foods.
- Other studies also suggest that D3 may be superior to D2. A 2016 studyTrusted Source notes that supplementation with vitamin D3 twice a week for 5 weeks was more effective in raising vitamin D levels in adults than the same amount of vitamin D2.
How common is vitamin D deficiency?
- Vitamin D deficiency is a problem all over the world.
- However, it’s pervasive in young women, infants, older adults, and people who have dark skin.
- About 42% of the U.S. population is vitamin D deficient. However, this rate rises to 82% in Black people and 70% in Hispanics, which systemic problems likely play a role in.
- If you have access to strong sun all year, then occasional sun exposure may be enough to fulfill your vitamin D requirements.
- However, your levels may fluctuate depending on the season if you live far north or south of the equator. The levels may go down during the winter months due to a lack of sufficient sunlight.
- In that case, you may need to rely on your diet (or supplements) and on what’s stored in body fat.
- In adults, a vitamin D deficiency may:
- cause muscle weakness
- intensify bone loss
- increase the risk of fractures
- In children, a severe vitamin D deficiency can cause delays in growth and rickets, a disease where the bones become soft.
- Furthermore, vitamin D deficiency is linked with several cancers, type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, high blood pressure, and thyroid problems.
How much of it should you take?
- How much vitamin D you need depends on many factors. These include:
- age
- ethnicity
- latitude
- season
- sun exposure
- clothing
- This is only a partial list of factors that help determine the amount of a person needs.
- The National Institutes of Health (NIH) recommends an average daily intake of 400–800 IU, or 10–20 micrograms (22, 23).
- However, some studies find that the daily intake needs to be higher if you aren’t being exposed to the sun or have darker skin tones.
- Depending on who you ask, blood levels above 20 ng/ml or 30 ng/ml are considered as “sufficient” (23, 24).
- In the same study, individuals who were it is deficient needed 5,000 IU to reach blood levels above 30 ng/ml.
- Studies in postmenopausal women with vitamin D levels below 20 ng/ml found that ingesting 800–2,000 IU raised blood levels above 20 ng/ml. However, higher doses were needed to reach 30 ng/ml (25, 26).
- People who are overweight or have obesity may also need higher amounts of vitamin D (27, 28).
- All things considered, a daily vitamin D intake of 1,000–4,000 IU, or 25–100 micrograms, should be enough to ensure optimal blood levels in most people.
- According to the National Institutes of Health, the safe upper limit is 4,000 IU. Make sure not to take more than that without consulting with a healthcare professional.
What are the optimal blood levels for It?
- Blood levels of vitamin D are assessed by measuring 25(OH)D in the blood, which is the storage form in the body.
- However, there’s been some debate over the definition of optimal blood levels.
- The Institute of Medicine (IOM) and the Nordic Nutrition Council base their recommendations on the following blood levels:
- sufficient: 25(OH)D greater than 20 ng/ml (50 nmol/l)
- insufficient: 25(OH)D less than 20 ng/ml (50 nmol/l)
- deficient: 25(OH)D less than 12 ng/ml (25 nmol/l)
- These organizations claim that blood levels of over 20 ng/ml meet the vitamin D requirements of more than 97.5% of the population.
- A committee at the IOM did not find higher blood levels associated with any additional health benefits.
- However, other experts, including the Endocrine Society, recommend aiming for higher blood levels closer to 30 ng/ml (75 nmol/l).
Can we get enough vitamin D from the sun alone?
- Summer sun exposure is the most effective way to get enough of it, but it doesn’t come without risk. Additionally, the amount of sunlight needed varies.
- Older individuals and dark-skinned people tend to produce less of it in the skin.
- Also, geographic location and season are crucial because production is affected in places further away from the equator.
- However, it doesn’t take a lot of sun exposure to make vitamin D, and it’s best to limit your time in the sun to 10 to 15 minutes, exposing your arms, legs, abdomen, and back.
- The Skin Cancer Organization recommends that you only do this two to three times weekly, followed by sunscreen use. After that period, your body will eliminate any excess vitamin D, and you’d be introducing sun damage without any added benefit.
- Remember that the same process that helps your body synthesize vitamin D can cause DNA damage, sunburn, and genetic mutations. This can cause wrinkles to develop and increase your risk for skin cancer.
- But you can opt to consume supplements or foods that contain vitamin D.
- It is is found in multivitamin/multimineral supplements. It is also available in dietary supplements containing only a few other nutrients. The two forms of in supplements are D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). Both forms increase vitamin D in your blood, but D3 might raise it higher for longer than D2. Because vitamin D is fat-soluble, it is best absorbed when taken with a meal or snack that includes some fat.
Vitamin D2 vs D3
- The two forms of it in supplements are D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol).
- Both forms increase of it in your blood, but D3 might raise it higher and for longer than D2.
- Because it is fat-soluble, it is best absorbed when taken with a meal or snack that includes some fat.
What happens if I take too much vitamin D?
- Taking too many it supplements over a long period can cause too much calcium to build up in the body (hypercalcaemia). This can weaken the bones and damage the kidneys and the heart.
- Ten micrograms a day will be enough for most people if you choose to take supplements.
- Please do not take more than 100 micrograms (4,000 IU) of vitamin D daily, as it could be harmful. This applies to adults, including pregnant and breastfeeding women and the elderly, and children aged 11 to 17 years.
- Children aged 1 to 10 years should not have more than 50 micrograms (2,000 IU) a day. Infants under 12 months should not have more than 25 micrograms (1,000 IU) daily.
- Some people have medical conditions that they may not be able to take as much safely. If in doubt, you should consult your doctor.
- If your doctor has recommended you take a different amount of it, you should follow their advice.
- You cannot overdose on it through exposure to sunlight. But always remember to cover up or protect your skin if you’re out in the sun for long periods to reduce the risk of skin damage and skin cancer.
Likely Effective for
- Bone loss in people taking drugs called corticosteroids. Taking it by mouth prevents bone loss in people taking drugs called corticosteroids. Also, taking it alone or with calcium seems to improve bone density in people with existing bone loss caused by corticosteroids.
- Weak and brittle bones (osteoporosis). Taking vitamin D3 by mouth and calcium seems to help prevent bone loss and bone breaks in people with osteoporosis.
- Psoriasis. Applying vitamin D in calcitriol, calcipotriene, paricalcitol, or paricalcitol to the skin can help treat plaque-type psoriasis. Applying itand corticosteroids seems to work better than using it or corticosteroids alone. But taking it by mouth doesn’t seem to help.
Possibly Effective for
- Cavities. Taking vitamin D2 or D3 by mouth reduces the risk of cavities by 36% to 49% in infants, children, and adolescents.
- Heart failure. Taking it by mouth can help reduce some people’s heart failure risk. But it doesn’t seem to help patients who already have heart failure.
- Bone loss in people with overactive parathyroid (hyperparathyroidism-related bone loss). Taking vitamin D3 by mouth reduces parathyroid hormone levels and bone loss in people with hyperparathyroidism.
- Infection of the airways. Taking it by mouth helps prevent respiratory infections in children. But taking it during pregnancy doesn’t seem to reduce the risk of these infections in children after birth. It also doesn’t help prevent diseases in adults.
- Preventing tooth loss (tooth retention). Taking calcium and vitamin D3 by mouth appears to avoid tooth loss in older adults.
Possibly Ineffective for
- Eczema (atopic dermatitis). Taking it during pregnancy or giving it to an infant doesn’t seem to reduce the chance of the child developing eczema.
- Heart disease. People with low blood levels seem more likely to develop heart disease. But taking supplements doesn’t prevent heart disease, heart attack, stroke, or other severe heart-related events in most people.
- Critical illness (trauma). Giving it to people with low vitamins levels who are in the hospital with an acute condition doesn’t make them more likely to live.
- Fractures. Taking it by mouth doesn’t prevent fractures in older people who do NOT have osteoporosis.
- High blood pressure. Taking it by mouth doesn’t seem to lower blood pressure in most people with high blood pressure. , But it might help people with deficient blood levels of vitamin D.
- Muscle strength. It alone does not seem to increase muscle strength in older adults.
- A mental disorder marked by hallucinations and delusion (psychosis). Taking it by mouth doesn’t seem to improve symptoms of psychosis in adults.
- Prostate cancer. Taking it by mouth doesn’t seem to reduce cancer progression or death from prostate cancer.
- Tuberculosis. it by mouth doesn’t help cure tuberculosis or make it less severe.
- There is interest in using it for several other purposes, but there isn’t enough reliable information to say whether it might be helpful.
Conclusion
- Vitamin D is a nutrient your body needs for building and maintaining healthy bones. That’s because your body can only absorb calcium, the primary component of bone when it is present. It also regulates many other cellular functions in your body. Its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and neuroprotective properties support immune health, muscle function and brain cell activity.
- It isn’t naturally found in many foods, but you can get it from fortified milk, cereal, and fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines. Your body also makes it when direct sunlight converts a chemical in your skin into an active form of the vitamin (calciferol).
- The amount for your skin depends on many factors, including the time of day, season, latitude, and skin pigmentation. Depending on where you live and your lifestyle, production might decrease or be completely absent during winter. Sunscreen, while essential to prevent skin cancer, also can reduce production.
- Many older adults don’t get regular exposure to sunlight and have trouble absorbing it. If your doctor suspects you’re not getting enough, a simple blood test can check the levels of this vitamin in your blood.
- Taking a multivitamin may help improve bone health. The recommended daily amount is 400 international units (IU) for children up to 12 months, 600 IU for people ages 1 to 70, and 800 IU for people over 70.
- Vitamin D is a vital essential nutrient that plays many critical roles in your body. As many people are deficient in this vitamin, supplements are sometimes needed to maintain optimal levels.
- The products above are among the best supplements on the market and suit various needs. Remember that it’s best to take supplements with a meal containing fat, such as olive oil or peanut butter, for optimal absorption.
- Before taking any new supplements, you must speak with a healthcare professional to determine whether — and how much — you need to supplement.
- Given the myriad of vitamins and minerals on the market, it can be tricky to determine which products are worth their price tags.
- Buying from reputable retailers and looking for vitamins made with high-quality ingredients can help ensure that you’re getting the best supplement possible.
- Checking the ingredient label and looking for products that have undergone third-party testing can also help you get the most bang for your buck.
Vitamin D 4000iu – 400 Premium Vitamin D3 Easy-Swallow Micro Tablets
400 Premium Vitamin D3 Easy-Swallow Micro Tablets – One a Day High Strength Cholecalciferol VIT D3
Incite Nutrition’s one-a-day extra-strong vitamin d tablets meet your daily needs as an easy-to-swallow serving. Whilst supporting the immune system’s normal functioning helps maintain strong bones and teeth and supports muscle function. Our D3 supplement does NOT contain Magnesium Stearate and is made in the UK with PREMIUM INGREDIENTS to the highest of standards. Incite Nutrition Vit D is Non-GMO and free from artificial colours, flavours, and preservatives.
- PREMIUM FORMULATION-We carefully sources our ingredients from our trusted UK suppliers. Our premium D3 supplement is Non-GMO and free from artificial colours, flavours and preservatives.
- 12 MONTH SUPPLY – No need to remember to re-order every month. One pot contains 400 tablets which will last you 52 weeks!
- UK PRODUCED-They Make all products in the UK, so you are safeguarded by high-quality standards. We ensure all our products conform with UK/EU legislation to maintain a high standard.
Vitamin D 4,000 IU, Maximum Strength Vitamin D3 Supplement
Vitamin D High Strength 4000iu – 400 Vitamin D3 Tablets (1+ Year Supply)
Read More:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship School
- Sepsis Training Program
- Download Pocket Guide for Antibiotic Pharmacotherapy Book
- Microbiology Course | ABC Bacteria
- Infectious Disease E-News | FREE Subscription
- ABC antimicrobials | Know all about the Antimicrobials
- Road Map to Antimicrobial Stewardship Training Program
- Register Now in FADIC Clinical Research School
- FADIC Drug Information Fellowship
- Buy FADIC Toolkit for Writing Research to Write a Great Research Paper
- Read 10 Skills You Must Learn to Do Research via Google Scholar in Arabic
- The FADIC Online Continuous Medical Improvement Programs & Mini-Courses.
- Check Now FADIC Book store and Buy books in different specialities.
- Watch Now FADIC TV to Keep Yourself Updated.
- FADIC Podcast focuses on varieties of pharmacist perspectives in different specialities.
- Subscribe Now to FADIC 2020 Daily News (FNN) and Keep Updated.
- Check Now about Coronavirus Resource Information Center.

 Log in
Log in Sign up
Sign up