Collagen: The Pros and Cons of Incorporating it in Your Health and Beauty Routine
“Collagen Benefits: The Ultimate Guide’
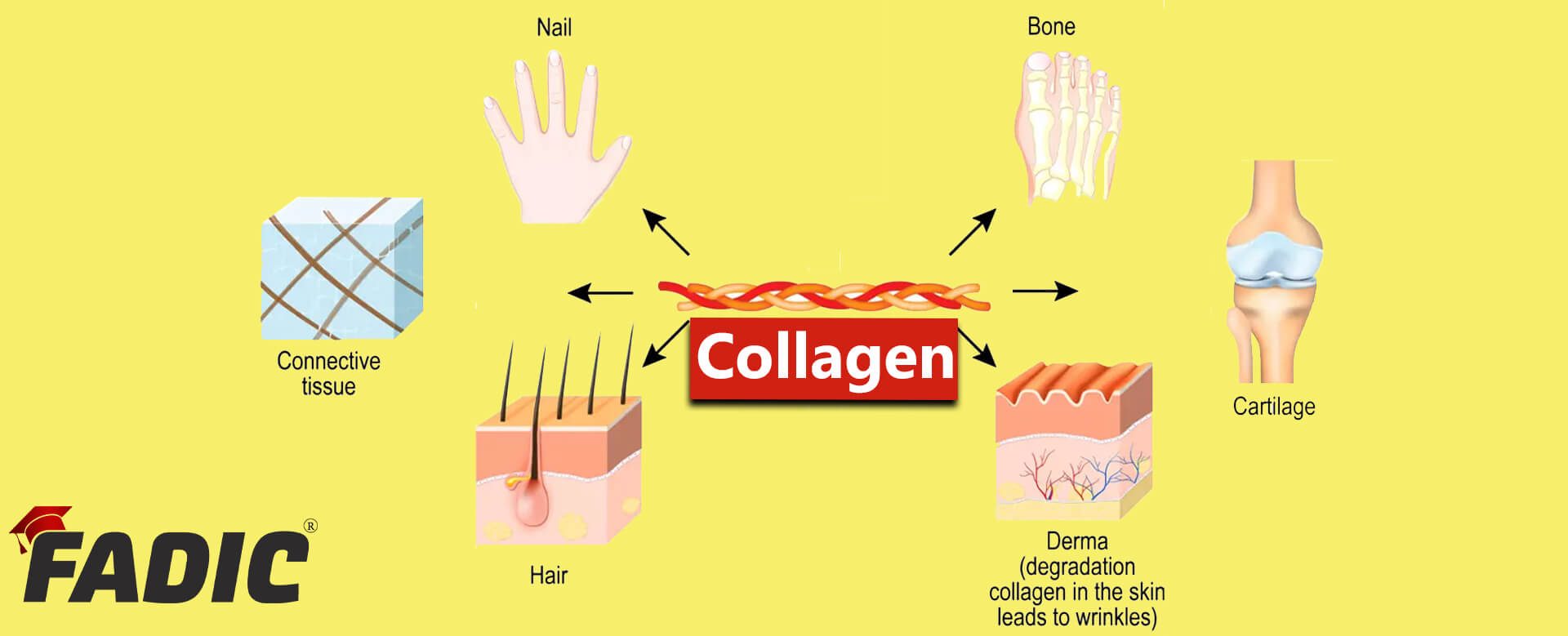
Understanding the Pros and Cons of Collagen for Skin, Hair, Joint and Overall Health
- What is collagen
- What causes collagen loss?
- Ultimate Guide To All The Types Of Collagen
- Health Benefits of Collagen: Pros, Cons
- Benefits of Collagen for Hair and Skin
- Collagen Supplements for Aging and Wrinkles
- Does Collagen Help With Acne
- How Collagen Helps With Healthy Joints & Bones
- Collagen for Your Skin: Healthy or Hype?
- Collagen Protein vs. Whey Protein: Which Is Better?
- Can collagen help your mental wellbeing?
- 13 Foods That Help Your Body Produce Collagen
- Are there benefits to taking collagen supplements?
- Best collagen supplements in the market
- Conclusion
Collagen Benefits: The Pros and Cons of Incorporating it in Your Health and Beauty Routine
- No doubt that forgetting is a great gift when it comes to overcoming painful experiences you had passed through. However, there is pathological memory loss that is referred to as “dementia”.
- More severe dementia is suspected to affect the patient’s quality of life and interfere with daily life activities. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia others being alcoholism, brain injury, vascular dementia, etc…
- Collagen is one of the very few food supplements. Benefits of Collagen can help ameliorate memory deficits.
Collagen: The Hidden Benefits You Need to Know Before Incorporating it in Your Diet
- Collagen, supplement, dementia, memory, amino acids, oxidative stress.
- How can collagen help in cases of memory deficits??
Biologically, collagen is the building block of connective tissue and makes up bones, tendons, skin, and blood vessels. - In the case of dementia, collagen supplements act on many aspects to enhance the condition where collagen reduces oxidative damage, maintains the integrity of blood vessels, and regulates the activity of key enzymes in the brain that are involved in the pathogenesis of dementia.
Collagen Benefits
- Collagen exerts antioxidant activity to attenuate oxidative stress. oxidative stress is a condition where reactive oxygen species load overwhelms antioxidants capacity and is involved in the pathogenesis of multiple forms of dementia “vascular and Alzheimer related dementia”.
- Additionally, collagen works to maintain brain perfusion and thus enhance metabolic activity and tissue health. Moreover, collagen regulates key enzymes and proteins involved in memory and attentional function such as acetylcholinesterase (AChE), phosphorylated cAMP-response element-binding protein (p-CREB), and brain- derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression.
- Furthermore, collagen as a rich source of amino acids especially the essential ones including glycine helps maintain cognitive performance. Indeed, glycine regulates the metabolic synthesis of specific nutrients that the brain and nerves use to produce energy and maintain the health of the brain.
What is Collagen ?
Figure 1 – illustartion of collagen amino acids – source Protein Data Bank

- Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body. It consisted of polypeptide substance comprising about one third of the total protein in mammalian organisms. .Its fibrous structure is used to build connective tissue which is a type of tissue connects other tissues and is a major component of bone, skin, muscle, tendon, and cartilage. It helps make hard tough tissue and elastic tissue.
- Collagen is naturally found only in animal flesh, such as meat and fish, which contain connective tissue.
What causes collagen loss?
Our bodies gradually produce less collagen as we age, but collagen production declines most rapidly due to:
- excessive sun exposure
- Smoking
- excessive alcohol
- lack of sleep and exercise
With aging, the collagen in the deep layers of the skin changes from a tightly organised network of fibers to a disorganised maze. Environmental exposure can damage collagen fibers, reducing their thickness and strength, leading to wrinkles on the skin’s surface.
Ultimate Guide To All The Types Of Collagen:
Right now 13 described collagens with at least 25 distinct genes are known. The collagen molecules can be categorised into four classes.
-
Class I :
flexible, strong, provides resistance to force, tension, and stretch; found in all connective tissue, notably scar tissue, tendons, ligaments, bone, cornea, skin, and dentin.
The molecules that make up banded collagen fibers, which are easily observable by standard electron microscopy.
With at least two and frequently three different collagen types present in each fibril, the banded fibers are heterogeneous in terms of collagen type.
It is thought that this multiplicity affects both the rate of fibril growth and the final diameter of the fibril.
-
Class II :
provides resistance to pressure, found in articular and hyaline cartilage of joints and intervertebral discs. Collagens are present and adhere to the banded fibrils’ surface.
-
Class III :
provides a flexible meshwork for cellular support, the main component of reticular fibers, often found in organs such as skin and blood vessels.
Also abundant during the early stages of wound healing and plays a role in granulation tissue formation.
Molecules that form separate fiber systems. Beaded filaments, anchoring fibrils, the basement membrane, and the network surrounding hypertrophic chondrocytes.
-
Class IV :
It is a meshwork that provides support and attachment to the underlying extracellular matrix forms the basal lamina of the basement membrane, an essential component of the kidneys, inner ear, and lens of the eye.
The various fiber types and consequently various types of collagen present in tissues are numerous. There are currently four known collagens in the bone cortex, which is no different from other tissues.
Health Benefits of Collagen: Pros, Cons:
As we said Benefits of Collagen represent a high percent of the vital proteins in human body so it is important in:
The Pros of Collagen
- Improving Skin Health
- Joint formation
- Bone formation and preservation
- Muscle formation
- Heart health
- Brain health
- Intestinal tissue health
On the other side, over usage of collagen supplements may cause Mild side effects could include:
The Cons of Collagen
- Bloating
- Heartburn
- feeling of fullness
- Sometimes Allergy
So Buy supplements that don’t contain your allergens if you suffer from food allergies.
Benefits of Collagen for Hair and Skin:
Skin care:
- Marine collagen (type I) is being presented as excellent functional ingredients, For example, in the medical field, it is often used for implants such as artificial skin grafts, wound dressings, and nerve conduits due to its low immunogenicity.
- In cosmetics, its properties take to the development of creams and gels with high moisturising action, but other activities such as anti-aging, anti-wrinkling, UV radiation protectors, and healing of wounds among other applications.
- Its inclusion in cosmetics formulations has to do with its film-forming properties, when applied covers the skin and decreases the trans-epidermal water loss, protecting skin from corrosive elements.
Hair Care:
- Provides Amino Acids that can be used to build hair. Collagen can act as an antioxidant and fight damage caused by free radicals. Prevent Hair Thinning Associated With Aging because Collagen makes up 70% of your dermis, the middle layer of your skin that contains the root of each individual hair.
- Collagen may be able to fight cell damage and slow graying. Due to its antioxidant properties.
Collagen Supplements for Aging and Wrinkles:
- The progression of skin aging is associated with decreased collagen density and dermal thickness in addition to a reduction in the synthesis and replacement of vital structural proteins.
- This causes the dermis to lose its integrity and pliability, which manifests itself clinically as lax and wrinkled skin.
- In many supplements, the bioactive ingredients are collagen peptides, which are peptides rich in the amino acids proline, glycine, and hydroxyproline.
- Upon digestion, these peptides are cleaved into di and tri-peptides, which are claimed to be used by the body as building blocks for proteins, such as collagen.
- It has been theorised that the availability of these protein peptides can help to maintain and increase the collagen in the skin.
- It is also believed that the peptides may increase hyaluronic acid production in skin fibroblasts, induce migration of fibroblasts, promote stronger collagen fibrils, and increase water content of the stratum corneum.
Does Collagen Help With Acne?
- Of course collagen can help to heal acne scars, Most of us need a few weeks following an outbreak for a scar to appear.
- The area begins to form new blood vessels that feed the skin. After several months, the area begins to produce collagen, which fills in the damaged skin.
- Additionally, it promotes the development of new tissue. Collagen can help scars look better right away by replacing lost volume.
- Fibroblasts, a type of skin cell, produce collagen to treat wounds when your skin is injured.
How Collagen Helps With Healthy Joints & Bones:
- It promotes the growth of cartilage Cartilage is a hard, rubbery substance that covers the ends of bones in joints. Age and repeated motion cause cartilage to lose its elasticity over time. In turn, this causes bones to rub against one another, tendons and ligaments to stretch, and pain to result.
- Collagen hydrolysate is of interest as a therapeutic agent of potential utility in the treatment of osteoarthritis and osteoporosis. Its high level of safety makes it attractive as an agent for long-term use in these chronic disorders.
Collagen for Your Skin: Healthy or Hype?
- Hydrolysed collagen (HC) is a popular ingredient considered to be an antioxidant. The high biocompatibility, simple biodegradability, and low antigenicity of this low molecular weight protein have led to its widespread use. It is a secure cosmetic biomaterial that effectively moisturises skin.
- Oral ingestion of HC increases the levels of collagen-derived peptides in the blood torrent and improves the skin properties such as elasticity, skin moisture, and transepidermal water loss.
- Additionally, daily intakes of HC protect the skin against UV melasma, enhances the fibroblast
- production and extracellular matrix of the skin. HC has been identified as a safe cosmetic ingredient
- for topical formulations with good moisturising properties at the stratum corneum layer of the skin.
Collagen Protein vs. Whey Protein: Which Is Better?
- Whey protein is a mixture of proteins isolated from whey, contains a variety of proteins that have been isolated. The proteins are immunoglobulins, serum albumin, -lactalbumin, and -lactoglobulin. Whey protein is frequently sold as a dietary supplement, and it has been linked to a number of health benefits.
- BUT Compared to whey protein, collagen powder has many more health advantages, and it is frequently a much better choice in terms of ingredients. A much better and more efficient alternative is collagen.
- Collagen is tasteless and odourless and has no additives or preservatives.
- As Collagen not only provides important amino acids, but it also can help in repairing and rebuilding bones and joints.
- It is dairy-free which is a good option for those who are lactose intolerant
- Benefits of Collagen has been shown to help improve the appearance of the skin, while whey protein can actually contribute to skin problems such as acne.
- The choice between collagen and whey protein is clear because collagen powder is so simple to incorporate into your diet and won’t even change the taste of your favorite foods.
Can collagen help your mental wellbeing?
- It is now generally acknowledged that the cytoarchitecture of the gray and white matter (GM and WM) reveals the state of the brain. It is believed that dendritic expanses and increases in neuronal synapses are indicators of good brain health because they lead to high plasticity of the synapses in the GM, which is thought to be a sign of flexibility in future learning
- As a result, the GM’s volume reflects the brain’s state of health . Myelinohgenesis, myelin remodeling, the proportion of oligodendrocytes and astrocytes, changes in fibrous tissue, and vascularisation are some of the factors that affect WM plasticity. Diffusion tensor imaging can be used to determine the network’s effectiveness at transmitting information about axonal fraction anisotropy between brain domains.
- According to many studies, collagen can improve mental health and increase cognitive function for the brain, It has been reported that the ingestion of Collagen hydrolysate (CH) may help recovery from brain injury by promoting angiogenesis , and that CH exerts neuroprotective action by suppressing inflammatory effects
13 Foods That Help Your Body Produce Collagen:
Collagen-rich foods come from animals. This includes meat from cows, fish, or chicken. The foods listed below all have high collagen content.
- Bone broth
- Fish and Shellfish
- Chicken
- Egg whites
- Citrus
- Tropical fruits
- Beans
- Cashews
- Leafy greens
- Berries
- Tomatoes
- Bell peppers
- Garlic
Are there benefits to taking collagen supplements?
Sadly, collagen starts to deteriorate as we get older. How quickly it deteriorates is influenced by a number of factors. As we age, our genes, for instance, produce collagen of lower quality. environmental factors, an unhealthy way of life, a poor diet, etc. as they produce free radicals, accelerates collagen deterioration.
The collagen-producing mechanism sustains significant damage as a result of these free radicals. As a result, our bodies need supplements that contain collagen.
So in addition to foods rich with collagen we can use collagen supplements to boost collagen formation. There are many dosages forms from collagen supplements, you can use it according to your purpose:
- Liquids
People who do not prefer eating tablets may take liquid collagen. You can massage them gently on the face. Another simple way is to mix the liquid in a glass of water and drink it.
- Gummies
Collagen gummies, also called chewable collagen, contain a little dose of sweetness. It is an ideal choice for people who dislike swallowing pills. Take 1-2 collagen gummies a day.
- Powder
The powdered form is the most popular way to take collagen due to its versatility. You can add a scoop of collagen powder to your daily diet by simply mixing it with smoothies, water, milk, or any drink. Since it lacks any specific flavour, adding powdered collagen to your drinks won’t make any taste difference. Taking 1-2 tablespoons of collagen is enough for a day. It is also convenient to mix powdered collagen with soft foods.
- Capsules
Collagen capsules or tablets are convenient for older adults to add extra collagen to their daily diet. You can take a maximum of two collagen capsules a day.
Best collagen supplements in the market:
- Care/of Collagen
- vital Proteins Collagen Peptides
- Vital Proteins Beauty Collagen Peptides Powder
- Garden of Life Grass Fed Collagen Beauty
- Thorne Collagen Plus
- Klean Collagen+C
- Anthony’s Hydrolyzed Marine Collagen Peptides
- HUM Nutrition Collagen Love
- Youtheory Collagen with Vitamin C
Conclusion
- Collagen is a very important protein and has many advantages as Rejuvenating skin, protecting joints, and bolstering bones and muscles.
- According to some studies, collagen supplements made from hydrolysed, easily absorbed collagen may promote everything from healthy skin to the development of more muscle mass.
Read More:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship School
- Sepsis Training Program
- Download Pocket Guide for Antibiotic Pharmacotherapy Book
- Microbiology Course | ABC Bacteria
- Infectious Disease E-News | FREE Subscription
- ABC antimicrobials | Know all about the Antimicrobials
- Road Map to Antimicrobial Stewardship Training Program
- Register Now in FADIC Clinical Research School
- FADIC Drug Information Fellowship
- Buy FADIC Toolkit for Writing Research to Write a Great Research Paper
- Read 10 Skills You Must Learn to Do Research via Google Scholar in Arabic
- The FADIC Online Continuous Medical Improvement Programs & Mini-Courses.
- Check Now FADIC Book store and Buy books in different specialities.
- Watch Now FADIC TV to Keep Yourself Updated.
- FADIC Podcast focuses on varieties of pharmacist perspectives in different specialities.
- Subscribe Now to FADIC 2020 Daily News (FNN) and Keep Updated.
- Check Now about Coronavirus Resource Information Center.

 Log in
Log in Sign up
Sign up