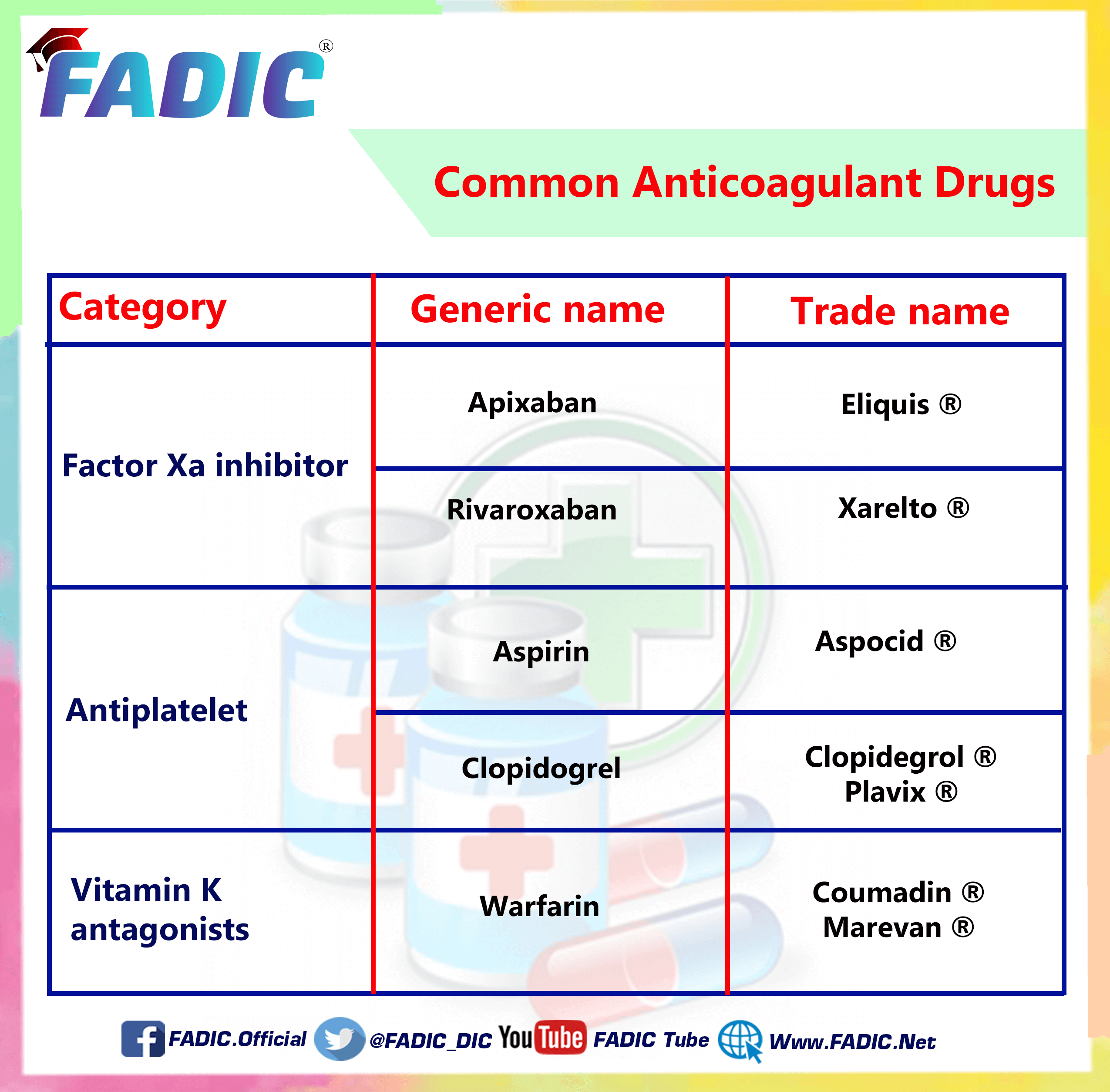
The Most Common Anticoagulant Drugs

The Most Famous 5 drugs for Anticoagulant are:

Aspirin

- Brand Names: Aspirin
- Therapeutic Category: Antiplatelet Agent; Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug (NSAID)
- Dosage Forms: Oral / Tablet Anticoagulant Drugs
- Use: Labeled Indications: Analgesic/Antipyretic/ Rheumatoid disease/ ischemic stroke/ transient ischemic attack/ acute myocardial infarction/ prevention of recurrent myocardial infarction/ Chronic coronary artery disease/
- Off-Label Indication: Acute coronary syndromes/ prevention of thromboembolism/ Carotid artery stenosis/ Pericarditis/ Preeclampsia (prevention)/ Prevention (primary) of cardiovascular disease
- Dosing : Adult : Analgesic and antipyretic: Oral: Immediate release: 325 to 650 mg as needed every 4 hours or 975 mg as needed every 6 hours or 500 to 1,000 mg as needed every 4 to 6 hours for no more than 10 days
- Coronary artery disease (CAD): Oral: 75 to 100 mg once daily
- Preeclampsia prevention: 75 to 150 mg once daily
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment:. avoid in patients with CrCl <10 mL/minute.
- Hepatic Impairment: Avoid use in severe liver disease.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Cardiac arrhythmia, edema, hypotension, tachycardia, Agitation, cerebral edema, coma, confusion, dizziness, fatigue
- Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset: Immediate release: Platelet inhibition: Within 1 hour
- Duration: Immediate release: 4 to 6 hours
- Bioavailability: Immediate release: 50% to 75%
- Half-life elimination: Parent drug: Plasma concentration: 15 to 20 minutes
- Important Notes:
- Low-dose aspirin for cardioprotective effects is associated with a two- to fourfold increase in UGI events.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: crosses the placenta / present in breast milk
- Medication Safety issue:
- Aspirin may be confused with Afrin

Warfarin

- Brand Names: Coumadin
- Therapeutic Category: Anticoagulant Drugs, Vitamin K Antagonist
- Dosage Forms: Oral / Tablet
- Use: Labeled Indications: Thromboembolic complications/ Myocardial infarction
- Off-Label Indication: Recurrent stroke/Transient ischemic attacks (secondary prevention)
- Dosing : Adult : Thromboembolic complications (prophylaxis/treatment) or myocardial infarction (risk reduction): Initial dosing must be individualized. Consider the patient (hepatic function, cardiac function, age, nutritional status, concomitant medications, risk of bleeding) : Start 2 to 5 mg once daily or for healthy individuals, 10 mg once daily for 2 days, then reduce dose.
- Geriatric: Oral: Initial dose ≤5 mg. Usual maintenance dose: 2 to 5 mg/day. Patients >60 years of age tend to require lower dosages to produce a therapeutic level of anticoagulation
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment:. No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Major hemorrhage, Purple-toe syndrome, systemic cholesterol micro-embolism, vasculitis, Chills, flatulence, nausea, vomiting
- Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: Initial anticoagulant effect on INR may be seen as soon as 24 to 72 hours
- Duration of action: 2 to 5 days
- Half-life elimination: 20 to 60 hours; Mean: 40 hours
- Time to peak, plasma: 4 hours
- Important Notes:
- Warfarin can cause major or fatal bleeding. Perform regular monitoring of international normalized ratio (INR) on all treated patients.
Drugs, dietary changes, and other factors affect INR levels achieved with warfarin therapy. Instruct patients about prevention measures to minimize the risk of bleeding
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Warfarin crosses the placenta / not present in breast milk
- Medication Safety issue: Coumadin may be confused with Cardura, Compazine, Kemadrin

Clopidogrel

- Brand Names: Plavix
- Therapeutic Category: Antiplatelet Agent
- Dosage Forms: Oral / Tablet
- Use: Labeled Indications: Acute coronary syndrome/ Recent myocardial infarction, recent stroke, or established peripheral arterial disease
- Off-Label Indication: Adjunctive therapy to support reperfusion with primary percutaneous coronary intervention/ Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (secondary prevention)/ stable ischemic heart disease/ Secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease (patients with diabetes and an aspirin allergy)/ Symptomatic carotid artery stenosis
- Dosing : Adult : Acute coronary syndrome :Initial: 300 mg or 600 mg loading dose, followed by 75 mg once daily for up to 12 months in combination with aspirin
- Coronary artery disease: Oral: 75 mg once daily
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment:. No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Gastrointestinal hemorrhage/ Minor hemorrhage/ Hematoma
- Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: loading dose: Detected within 2 hours
- Duration of action: Platelet aggregation and bleeding time gradually return to baseline after 5 days after discontinuation.
- Half-life elimination: Parent drug: 6 hours
- Time to peak, serum: 0.75 hours
- Important Notes:
- Clopidogrel increases the risk of bleeding. Use is contraindicated in patients with active pathological bleeding
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Use is not recommended/ not known if present in breast milk
- Medication Safety issue: Plavix may be confused with Elavil, Paxil, Pradax (Canada), Pradaxa

Rivaroxaban

- Brand Names: Xarelto
- Therapeutic Category: Anticoagulant Drugs, Factor Xa Inhibitor
- Dosage Forms: Oral / Tablet
- Use: Labeled Indications: Coronary artery disease (chronic) or peripheral artery disease/ Indefinite anticoagulation/ Nonvalvular atrial fibrillation/ Venous thromboembolism
- Off-Label Indication: Acute coronary syndrome / Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia / Superficial vein thrombosis
- Dosing : Adult : Acute coronary syndrome: Oral: 2.5 mg twice daily; administer in combination with low dose aspirin plus clopidogrel
- Nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AF) (to prevent stroke and systemic embolism): Oral: 20 mg once daily with the evening meal.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): Oral: 15 mg twice daily with food for 21 days followed by 20 mg once daily with food
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment:. Acute coronary syndrome : CrCl <30 mL/minute: Avoid use.
- Coronary artery disease (chronic) or peripheral artery disease: CrCl ≥15 mL/minute: No dosage adjustment necessary; use with caution in severe impairment.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): CrCl <30 mL/minute: Avoid use.
- Hepatic Impairment: Moderate to severe impairment: Avoid use.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Hemorrhage/ Dizziness/ insomnia /anxiety / Abdominal pain
- Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Half-life elimination: Terminal: 5 to 9 hours
- Time to peak, plasma: 2 to 4 hours
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Important Notes:
- Epidural or spinal hematomas have occurred in patients treated with rivaroxaban who are receiving neuraxial anesthesia or undergoing spinal puncture. These hematomas may result in long-term or permanent paralysis.
- Premature discontinuation of any oral anticoagulant, including rivaroxaban, increases the risk of thrombotic events
- Pregnancy & Lactation: rivaroxaban crosses the placenta / present in breast milk

Apixaban

- Brand Names: Eliquis
- Therapeutic Category: Anticoagulant, Factor Xa Inhibitor
- Dosage Forms: Anticoagulant, Factor Xa Inhibitor
- Use: Labeled Indications: Deep vein thrombosis/ Nonvalvular atrial fibrillation/ Postoperative venous thromboprophylaxis following hip or knee replacement surgery/ Pulmonary embolism
- Off-Label Indication: Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia/ Recurrent stroke/transient ischemic attacks
- Dosing : Adult : Nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (to prevent stroke and systemic embolism): Oral: 5 mg twice daily
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) treatment: 10 mg twice daily for 7 days followed by 5 mg twice daily.
- Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing. If patient is ≥80 years of age and either weighs ≤60 kg or has a serum creatinine ≥1.5 mg/dL, then reduce dose to 2.5 mg twice daily.
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment:. DVT: No dosage adjustment
- Nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: Serum creatinine ≥1.5 mg/dL and either ≥80 years of age or body weight ≤60 kg: 2.5 mg twice daily.
- Hepatic Impairment: Severe impairment: Use is not recommended.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Hemorrhage/ Nausea/ Increased gamma-glutamyl transferase/ Epistaxis
- Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 3 to 4 hours
- Bioavailability: 50%
- Half-life elimination: 12 hours
- Time to peak: 3 to 4 hours
- Important Notes:
- Bleeding: May increase the risk of bleeding, including severe and potentially fatal bleeding. Concomitant use of drugs that affect hemostasis increases the risk of bleeding.
- Premature discontinuation of any oral anticoagulant, including apixaban, in the absence of adequate alternative anticoagulation increases the risk of thrombotic events.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Pregnancy Risk Factor B/ not known if present in breast milk.
- Drug safety issue: Apixaban may be confused with axitinib

Read More
Copyright ©: All content on FADIC Website, including medical opinion and any other health-related information, and drug Informtation is for informational purposes only

 Log in
Log in Sign up
Sign up