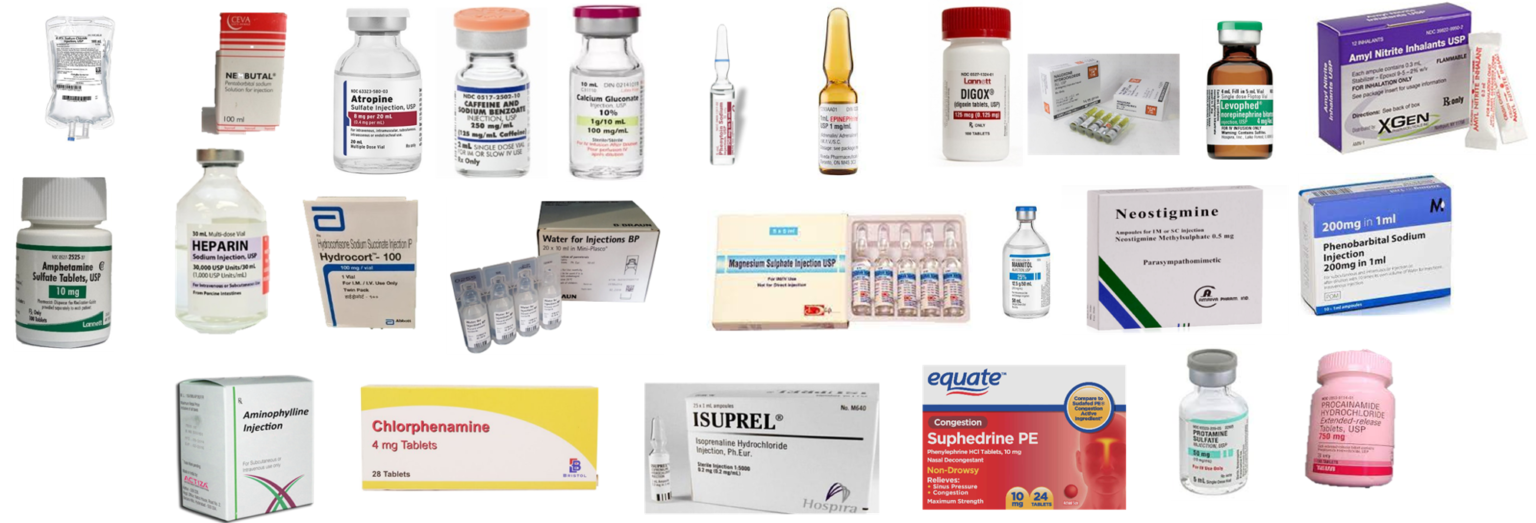
Most Important Emergency Drugs and Aids

Most Important Emergency Drugs and Aids
Managing medical emergencies requires knowledge and skills of the most used emergency drugs and pharmaceutical aids.
This article is a brief guide to emergency drugs and pharmaceutical aids every physician should know.
The dosages mentioned below are guides only. Drug therapy should constantly adjust to the individual patient’s condition.
You should prepare the emergency drugs box to be ready for any urgent situations.
1-Most Common Emergency Drugs:
- Aminophylline
- Amphetamine sulfate
- Amyl nitrite inhalation
- Atropine sulfate
- Caffeine sodium benzoate
- Calcium Gluconate
- Chlorpheniramine
- Digoxin
- Diphenylhydantoin sodium
- Phenylephrine
- Epinephrine
- Heparin
- Hydrocortisone
- Isoproterenol
- Magnesium sulfate injection
- Mannitol injection
- Nalorphine
- Neostigmine
- NorEpinephrine
- Phenobarbital
- Pentobarbital
- Procainamide
- Protamine injection
- Saline for injection
- Water for injection
2-Pharmaceutical Aids:
These aids are very helpful in the anaesthetic emergency drugs.
- Syringes and Needles
- Venous cannulation
- Oxygen catheter
- Urine catheter
- Indwelling catheter
- External catheters (condom catheters)
- Short-term catheters (intermittent catheters)
- Sterile suction catheter
- Razor suction blades
- Sterile gelatin sponge
- Resuscitation tube
- Oxygen equipment
- Burn sheets
- Surgical instruments like scissors and forceps

1- List of emergency drugs:
Some organisations prepare the list of these emergency drugs, such as CQC emergency drugs, it is important to know the Most Important Emergency Drugs and Aids.
Aminophylline
Brand names: Elixophyllin, Theo-24, Slo-phyllite, Uniphyl
Indications:
- A bronchodilator treats acute asthma, emphysema, and chronic bronchitis.
- Aminophylline is indicated for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Mechanism of action:
- Aminophylline is used for the systemic treatment of obstructive airway diseases. Bronchodilation is mediated through smooth muscle relaxation and inhibition of phosphodiesterase isoenzymes (type III and type IV). Relaxation of the bronchial airways and pulmonary blood vessels.
- Moreover, aminophylline blocks adenosine-mediated bronchoconstriction and activates histone deacetylase to prevent the transcription of inflammatory genes.
Dose:
Aminophylline dose is 5.7 mg/kg (ideal body weight) intravenously (IV) over 30 minutes, max 500mg.
Side effects:
- Nausea
- Insomnia
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Hypokalemia
- Cardiac arrest
- Seizures
Highly recommend an Online Marketing tool from SEMRUSH.
Emergency drugs list
Amphetamine sulfate
Brand names: Evekeo, Evekeo ODT, Adzenys XR-ODT and Dyanavel XR.
Indications: A central nervous system (CNS) stimulant medication. This drug is used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and narcolepsy. Amphetamine is also used in the treatment of cyanide poisoning.
Mechanism of action:
Amphetamine changes the level of neurotransmitters in the brain, enhancing attention and focus.
Dose:
Amphetamine dose is 5 to 60 milligrams divided daily, depending on the individual patient’s response.
Side effects:
- Chest pain and shortness of breath
- Aggressive behaviour
- Difficulty sleeping, nightmares, and restlessness
- Loss of appetite and psychosis
Important notes:
This medicine must be avoided if the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, using or has used a monoamine oxidase inhibitor within the past 14 days additionally if the patient has glaucoma or an overactive thyroid gland.
Amyl nitrite inhalation
Brand names: Amyl Nitrite
Indications:
Amyl nitrite is a vasodilator used for the relief of angina pectoris.
Mechanism of action:
Amyl nitrite dilates involuntary smooth muscles, thus increasing blood and oxygen supply to the heart. Moreover, it reduces heart workload and relieves angina pain.
Dose:
Adults’ dosage is one ampule (0.3 millilitres) by inhaling the vapour of amyl nitrite through the nose. If pain is not relieved, the dose must be repeated within 1 to 5 minutes.
Side effects:
- Dizziness and headaches
- Nausea and vomiting,
- Shortness of breath, blurred vision
- Low blood pressure
- Psychological effects
Important notes:
- Additionally, if the patient has glaucoma or cerebral haemorrhage. As this drug may transiently increase intraocular and intracranial pressures.
Atropine sulfate
Brand names: Atropine Atnaa, Busulfex, Motofen, Donnatal, Atropine, Duodote, Isopto Atropine, Elon-plus, Minims Atropine Sulfate, Lomotil, Phenohytro.
Indications:
Atropine is used as a first-line drug for treating acute severe bradycardia, acting as an anticholinergic drug. Atropine is also used in organophosphate-carbamate toxicity. Additionally, atropine acts as an antispasmodic agent.
Mechanism of action:
- Atropine blocks the effects of the vagus nerve on the heart, blocking all the cholinergic receptors.
- Atropine counteracts peripheral blood dilatation and abrupt decrease in blood pressure through its anticholinergic effect.
Dose:
The atropine sulfate dose is 0.02 mg/kg/IV; you may repeat x 1 dose in 3 minutes. Atropine sulfate doses from 0.5 to 1 mg for anti-vagal effects and from 2 to 3 mg as an antidote for organophosphorus or muscarinic mushroom poisoning.
Side effects:
- Rapid heart rate
- Headache and drowsiness
- Hypersensitivity reactions
- Sensitivity to light
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
Important notes:
Atropine is one of the Most Important Emergency Drugs and Aids.
It should be used cautiously in acute coronary ischemia and myocardial infarction since increased heart rate may worsen ischemia. Moreover, it may increase the zone of infarction.
Caffeine sodium benzoate
Brand names: Caffeine and Sodium Benzoate Injection
Indications:
Caffeine and sodium benzoate injection is used to treat acute respiratory depression associated with overdosage of CNS depressant agents (e.g., opiate analgesics or alcohol) and with an electric shock. In addition, this drug provides mental alertness for patients suffering from fatigue.
Mechanism of action:
- Caffeine inhibits phosphodiesterase, which degrades cyclic 3′- 5′ adenosine monophosphate (AMP).
- The caffeine effect is mediated by increasing intracellular cyclic- 3′- 5′ AMP levels. Caffeine stimulates all levels of the CNS.
- Caffeine stimulates vasomotor, medullary vagal, and respiratory centres in larger doses. Thus, promotes bradycardia, and vasoconstriction improves diaphragmatic contractility and increased respiratory rate.
Dose:
IV or IM dose: 500 mg-1 g (250–500 mg).
Side effects:
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Tachycardia
- Nausea and gastric irritation
- Insomnia and anxiety
- Restlessness, nervousness, and seizures
Important notes:
Caution in pregnancy and patients with cardiovascular disease and heart rhythm problems.
Calcium Gluconate
Brand names: Calcium gluconate
Indications:
- Calcium gluconate is used for ventricular arrhythmias and reduces the risk of ventricular fibrillation.
- Moreover, it is used in the treatment of tetany and hypocalcemia.
- Management of dysrhythmia and cardiotoxicity due to hyperkalemia or hypermagnesemia.
Mechanism of action:
- Calcium is essential for maintaining the functional integrity of the nervous, muscular, and skeletal systems.
- Also, the cell membrane and capillary permeability.
- Moreover, calcium is a coenzyme for several enzymatic reactions and physiologic processes.
- Including the transmission of nerve impulses, cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscle contraction, renal function, respiration, and blood coagulation.
- Additionally, normal mineralisation of bone depends on adequate amounts of total body calcium.
- Also, calcium gluconate works by raising calcium levels in the blood, binding to excess magnesium or potassium.
Dose:
500 to 2000 mg oral dose 2 to 4 times a day.
- 100 mg/kg/dose IV. May repeat x 1 dose.
- Calcium gluconate slow IV push, infuse over 30-60 minutes for other indications. Stop infusion if the heart rate is more significant than 100 bpm.
Side effects:
- Nausea, diarrhoea, and decreased appetite
- Bradycardia
- Irregular heartbeats
- Paresthesia
Important notes:
Systemic calcium levels should be monitored as hypercalcemia causes ECG changes and variable degrees of heart block.
Calcium supplementation should be avoided in severe kidney disease and hyperparathyroidism.
Chlorpheniramine
Brand names: Allerief, Allercalm, Hayleve, Pollenase, Piriton
Indications:
Chlorpheniramine is the Most Important Emergency Drugs and Aids.
It treats symptoms of allergic reactions (hay fever, rhinitis, asthma, and urticaria).
Symptoms include runny nose, sneezing, watery eyes, itching, and allergic conjunctivitis.
Mechanism of action:
Chlorpheniramine is an antihistamine or a histamine H1 antagonist.
Chlorpheniramine binds to the histamine H1 receptor, which blocks the action of endogenous histamine and relieves allergic symptoms.
Dose:
Chlorpheniramine dose for adults and children over 12 years is one tablet or 10 ml liquid medicine (4 mg) every 4-6 hours.
Side effects:
- Dizziness and disturbed coordination
- Dry mouth
- Drowsiness, tremors, and fatigue
- Palpitations and mood changes
- Nervousness or restlessness
Important notes:
Cautiously use this drug if the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding. It must be avoided for patients having narrow-angle glaucoma.
Digoxin
Brand names: Digitek, Digox, Lanoxicaps, Lanoxin, Cardoxin
Indications:
Digoxin is the Most Important Emergency Drugs and Aids.
It used to manage atrial fibrillation, arrhythmias, congestive heart failure, and abortion.
Mechanism of action:
- Digoxin works by changing sodium and potassium levels inside heart cells.
- This effect improves the strength and efficiency of the heart rate and rhythm.
- Thus, it enhances blood circulation and reduces swelling of the hands and ankles in patients with heart problems.
- Moreover, digoxin reversibly inhibits the activity of the myocardial Na-K ATPase pump, which induces an increase in intracellular sodium.
- This effect will drive an influx of calcium in the heart and cause an increase in contractility.
- Cardiac output increases with a decrease in ventricular filling pressures.
- Digoxin helps decrease norepinephrine levels by activating the parasympathetic nervous system.
- Thus, leading to sinoatrial and atrioventricular node effects and decreased heart rate.
- Another use of digoxin is to induce fetal death before a second-trimester abortion. Digoxin kills the cells and poisons the tissues of the fetus.
Dose:
The initial digoxin dose is 10 -15 micrograms per kg given IV over 20 to 30 minutes.
Side effects:
- Dizziness, drowsiness, and headache
- Loss of appetite and vomiting
- Diarrhoea and stomach pain
- Unusual weight gain and oedema
- Difficulty breathing
Diphenylhydantoin sodium
Brand names: Dilantin, Phenytek
Indications:
- 5,5-Diphenylhydantoin sodium salt is an antiepileptic drug.
- An anticonvulsant that is used to prevent and control seizures.
- It is also an anti-arrhythmic and muscle relaxant.
- Also other indications include bipolar disorder, retina protection, and wound healing.
Mechanism of action:
- 5,5-Diphenylhydantoin sodium salt is an anticonvulsant / antiepileptic drug. This drug is a potent voltage-gated Na+ channels blocker.
- Limits seizure activity by promoting sodium efflux from neurons in the motor cortex.
- Thereby stabilising the neuron and inhibiting synaptic transmission.
- Moreover, this reduces the activity of brainstem centres responsible for the tonic phase of seizures.
- Thus, inhibition of repetitive firing of action potentials inhibits the spread of seizure activity.
Dose:
- The oral drug dose is 1 g divided into three doses (400 mg, 300 mg, 300 mg) at 2-hour intervals. The usual maintenance dosage started 24 hours after the loading dose.
- IV loading dose: 10 to 15 mg/kg IV slowly.
- Maintenance dose: 100 mg IV every 6 to 8 hours.
Side effects:
- Dyspnea
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and constipation
- Dry mouth
- Weight gain or loss
- Eye pain, conjunctivitis, photophobia
- Tinnitus, headache, fatigue, and dizziness
- Drowsiness, ataxia, confusion, insomnia
- Irritability, nervousness, numbness, and psychotic disturbances
- Tremor and oedema,
- Chest pain, tachycardia, and hypotension
Important notes:
Seizure control is crucial during pregnancy.
Thus, avoid a sudden stop in drug use during pregnancy.
This drug is not safe for breastfeeding patients.
Phenylephrine
Brand names: Neo-Synephrine, Pretz-D, Rhinall, Nostril, Tur-Bi-Cal, Vicks Sinex
Indications:
Phenylephrine is the Most Important Emergency Drugs and Aids.
It relieves nasal congestion caused by colds, allergies, and hay fever.
Mechanism of action:
- It works by reducing swelling of the blood vessels in the nasal passages.
- Phenylephrine is an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor agonist that mediates vasoconstriction. Raising systolic and diastolic pressure, peripheral vascular resistance, and stroke output.
- Moreover, increased blood pressure stimulates the vagus nerve, causing reflex bradycardia.
Dose: 10 mg oral dose every 4 hours; maximum dose is 60 mg per 24 hours.
Side effects:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Irregular heartbeat
- Flushing
- Tingling, restlessness, and nervousness
- Insomnia
- Increased blood pressure
Epinephrine
Brand names: Adrenalin, Adrenalin Chloride, Audi-Q, Symjepi, Adrenaclick, Epipen, Epipen Jr
Indications:
- Epinephrine injection is an emergency treatment for type 1 hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis.
- Moreover, injection induces and maintains mydriasis during intraocular surgeries.
- Epinephrine injection increases blood pressure in patients with hypotension, septic shock, and cardiac arrest.
Mechanism of action:
- Epinephrine is an alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonist (sympathomimetic agent). Epinephrine injection relaxes the smooth muscle of the bronchi and iris.
- Epinephrine is a histamine antagonist used to treat allergic reaction symptoms.
- This drug leads to bronchial smooth muscle relaxation that helps to relieve bronchospasm. Also, reduces wheezing and dyspnea that may occur during anaphylaxis.
Dose:
- 0.1mg/mL (1mg/10mL); 1: 1000 (1mg/ml), auto-injector 0.3 mg/ml (EpiPen), 0.15 mg/ml (EpiPen Jr).
- For anaphylaxis treatment, epinephrine is injected intramuscularly into the anterolateral aspect thigh or subcutaneously.
- For cardiovascular life support, epinephrine is injected IV.
Side effects:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache and tremor
- Nervousness, palpitations, and seizures
- Tingling and numbness
- Fast heartbeat and high blood pressure
Heparin
Brand names: Heparin Leo, Hep-Pak, Hep-Pak CVC, Heparin Lock Flush, Heparin Sodium ADD-Vantage
Indications:
- Heparin injection is an anticoagulant.
- Used in preventing and treating thrombotic events such as venous thromboembolism, pulmonary embolism, and atrial fibrillation.
- Moreover, heparin prevents clotting during surgical procedures (cardiac surgery), extracorporeal circulation, or dialysis, including continuous renal replacement therapy.
Mechanism of action:
- Heparin is an anticoagulant used for thromboprophylaxis and to treat thrombosis.
- Heparin binds to antithrombin and blocks specific factors in the clotting cascade: thrombin (Factor IIa) and Factor Xa.
- Thereby, Inactivating thrombin blocks the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin; this prevents the formation of clots and prolongs the coagulation time.
- Also, heparin prevents the formation of a stable fibrin clot by inhibiting the activation of the fibrin stabilising factor.
Dose:
Heparin drips in venous thromboembolism initiated with an injection of 80 units/kg IV x 1, followed by a continuous infusion rate of 18 units/kg/hour.
Side effects:
- Nausea and bloody vomiting
- Pain and bruising
- Blood in urine or stool
- Coughing up blood
- Fatigue
Hydrocortisone
Brand names: A-Hydrocort, SoluCORTEF
Indications:
- Moreover, this glucocorticoid is anti-inflammatory and used for treating dermatoses, endocrine disorders, and immune conditions.
- In addition, blood or bone marrow problems, inflammatory eye issues, and allergic disorders.
Mechanism of action:
- Hydrocortisone is a corticosteroid drug.
- This drug binds to the glucocorticoid receptor producing an anti-inflammatory effect by decreased vasodilation and leukocyte migration to sites of inflammation.
- Moreover, hydrocortisone treats allergic reactions and relieves swelling, itching, and redness.
- Hydrocortisone inhibits neutrophil apoptosis and binds to the glucocorticoid receptor leading to the inhibition of NF-Kappa B and other inflammatory transcription factors.
- Additionally, they promote anti-inflammatory genes like interleukin-10.
Dose:
Hydrocortisone’s usual dose is 50 to 100 mg IV for 6 hours.
Side effects: Increased appetite, fluid retention, rapid weight gain, headache, dizziness, and shortness of breath. Important notes:
Isoproterenol
Brand names: Isuprel
Indications: Isoproterenol is a drug used to treat bradycardia and heart block.
Mechanism of action: Isoproterenol is a catecholamine. A non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor agonist is used for cardiac arrest or block.
Isoproterenol produces its effect by:
- Increased heart contractility; thus, heart rate increases.
- Peripheral vasodilation and relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle.
Dose:
Isoproterenol intravenous injection is five mcg/min (1.25 mL of a 1:250,000 dilution), then a dose of 2-20 mcg/min based on the patient’s response.
Side effects:
- Nausea and gastric upset
- Headache and dizziness
- Fatigue
- Nervousness
- Blurred vision
- Ventricular arrhythmia
- Insomnia
Magnesium sulfate injection
Brand names: Magnesium Sulfate
Indications:
- Magnesium sulfate injection is indicated to control life-threatening seizures /convulsions immediately.
- This injection treats severe toxaemias (pre-eclampsia and eclampsia) during pregnancy.
Mechanism of action:
- Magnesium sulfate injection treats convulsions by reducing muscle contractions and blocking peripheral neuromuscular transmission.
- It reduces acetylcholine release at the myoneural junction.
- Additionally, Magnesium inhibits calcium influx, thus acting as vascular smooth muscle.
Dose:
The intravenous injection of magnesium sulfate is 1 to 4 g in a 10% to 20% solution.
Side effects:
- Flushing
- Numbness
- Extreme drowsiness
Mannitol injection
Brand names: Mannitol IV, Osmitrol
Indications:
- Mannitol injection treats elevated intracranial, intraocular pressure, and cerebral oedema.
Mechanism of action:
- Mannitol is a diuretic that reduces pressure and swelling around the brain and the eyes.
- Mannitol injection elevates blood plasma osmolality and enhances water flow from the brain and cerebrospinal fluid into the interstitial fluid and plasma.
- Thereby reducing cerebral oedema, intracranial pressure, and cerebrospinal fluid volume and pressure.
- Moreover, mannitol prevents the concentration of toxic substances in the tubular fluid thus, prevent nephritis.
- Mannitol induces diuresis by facilitating water excretion, inhibiting the renal tubular reabsorption of sodium, chloride, and other solutes.
- Also, in cystic fibrosis, mannitol produces an osmotic gradient across the airway epithelium that draws fluid into the extracellular space, allowing more straightforward mucociliary clearance.
Dose:
Mannitol injection dosage ranges from 50 to 200 g within a 24-hour.
Side effects:
- Headache
- Nausea
- Blurred vision
- Irregular heartbeat
- Dizziness
- Hypotension.
Important notes: Monitoring cardiac and renal function is essential as the drug may cause dehydration and osmotic nephrosis.
Nalorphine
Brand names: Nalorphine, Naloxone
Indications:
Nalorphine is used in the treatment of severe acute respiratory depression.
Mechanism of action: Nalorphine is an opioid receptor agonist that causes supraspinal analgesia.
Dose:
The Nalorphine dose is 5-10 mg, repeated every 10-15 minutes until respiration is restored. The maximum amount is 40 mg.
Side effects:
- Nausea
- Headache
- Cramps
- Drowsiness
- Respiratory depression
- Miosis.
Neostigmine
Brand names: Prostigmin, Bloxiverz
Indications:
- Neostigmine is a cholinesterase inhibitor. Indicated for symptomatic treatment of myasthenia gravis, improves muscle tone.
Mechanism of action:
- Neostigmine inhibits acetylcholinesterase, which leads to acetylcholine build-up at the neuromuscular junction.
- Neostigmine overcomes the competitive inhibition of nondepolarising blocking drugs.
- Neostigmine stimulates both muscarinic and nicotinic receptors involved in muscle contraction.
Dose: Intravenous dose is 0.03 mg/kg to 0.07 mg/kg, up to 5 mg.
Side effects:
- Nausea
- Abdominal cramps
- Dizziness
- Itching
- Headache
- Shortness of breath and irregular heartbeat
- Seizures
NorEpinephrine
Brand names: Levophed, Levarterenol
Indications:
Norepinephrine is used to treat critical hypotension.
It constricts blood vessels and maintains blood pressure in case of emergency hypotension.
It also increases alertness, arousal, and attention.
Mechanism of action:
- It is an inotropic stimulator of the heart and dilator of coronary arteries because of its activity at the beta-adrenergic receptors.
Dose: 1-30 mcg/min IV
Side effects:
- Headache and blurred vision
- Irritation and numbness
- Irregular heart rate
- Problems with vision, speech, or balance
- Insomnia
Phenobarbital
Brand names: Donnatal, Luminal, Phenobarb, Phenohytro
Indications:
Phenobarbital a long-lasting barbiturate. An anticonvulsant is used in the treatment of all types of seizures. Inducing sedation, hypnosis, and anaesthesia.
Mechanism of action:
- Phenobarbital is a nonselective central nervous system depressant.
- Phenobarbital inhibits gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors and modulates chloride currents through receptor channels. Therefore, it inhibits glutamate-induced depolarisations.
Dose:
The phenobarbital dose is 20 mg/kg IV Xan additional oral dose may of 5-10 mg/kg dose in 20 minutes may be needed (max dose 30 mg/kg); max infusion rate 50 mg/min.
Side effects:
- Numbness
- Shallow breathing
- Dizziness and loss of coordination
- Drowsiness
- Skin rash
Pentobarbital
Brand names: Nembutal, Nembutal sodium
Indications:
- Pentobarbital is a barbiturate drug used to treat short-term insomnia and as a pre-anaesthetic for surgery.
- Moreover, this drug is a central nervous system depressant.
- Induces sedation and relieves tension or nervousness.
- Also used for control of certain types of seizures.
- Pentobarbital is used at high doses as an anticonvulsant for emergency seizure control and induced comas.
Mechanism of action:
- Pentobarbital induces suppression of glutamatergic neurotransmission through direct inhibition of excitatory AMPA-type glutamate receptors.
- Pentobarbital action is acute potentiation of inhibitory GABAergic tone.
- Pentobarbital inhibits glutamate, responsible for nerve depolarisation in the voltage-activated calcium currents.
Dose:
The intravenous dose of pentobarbital should not exceed 50 mg/minute.
A slow IV injection in the undiluted form.
Side effects:
- Drowsiness
- Hallucinations
- headache and dizziness
- Insomnia
- Nausea and vomiting
- Restlessness
- Respiratory depression
- Bradycardia
Procainamide
Brand names: Procan, Pronestyl
Indications:
- Procainamide is used for the treatment of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.
- Procainamide is a sodium channel blocker.
- Procainamide is indicated to produce local or regional anaesthesia.
- Moreover, used in treating ventricular tachycardia during cardiac surgery or catheterisation in myocardial infarction and heart diseases.
Mechanism of action:
- Procainamide is a sodium channel blocker.
- This drug possesses an antiarrhythmic effect.
- Moreover, it stabilises the neuronal membrane by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required to initiate and conduct impulses.
- Thereby affecting local anaesthetic action.
Dose:
The Procainamide dose is 100 mg/dose at a 50 mg/minute rate repeated every 5 minutes.
Side effects:
- Irregular heartbeats
- Bitter taste
- Vomiting and loss of appetite
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Stomach upset
Protamine injection
Brand names: Protamine
Indications:
Protamine sulfate injection is indicated for counteracting the anticoagulant effect of heparin for treating heparin overdose.
Mechanism of action:
Protamine sulfate injection is an antidote to heparin.
It binds to heparin; this inactive complex between protamine sulfate and heparin produces an anticoagulant effect.
This effect helps treat haemorrhages caused by heparin overdose.
Dose:
1 to 1.5 mg of protamine per 100 units of heparin if heparin is administered by deep subcutaneous injection.
Administering a portion of the dose slowly IV, then the remaining infusion over 8 to 16 hours.
Side effects:
- Dizziness
- Unusual bleeding or bruising
- Breathing problems and chest pain
- Fatigue
Saline for injection
Brand names: Normal Saline, Sterile Saline
Indications:
- Saline is indicated for diluting or dissolving drugs for intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous injection.
- Sodium chloride injection (saline) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for fluid and electrolyte replenishment for intravenous administration.
Mechanism of action:
- Emergency treatment of severe salt depletion caused by excess sweating, vomiting, and diarrhoea.
- Also, saline is used in the treatment of hyponatremia and hypochloremia.
- Saline is used for flushing intravascular catheters.
- A sterile, isotonic single-dose vehicle, solvent, or diluent for intravenously, intramuscularly, or subcutaneously administered drugs.
Dose:
Saline is used as directed by a physician.
The dosage depends upon the patient’s age, weight, clinical condition, and laboratory data.
Side effects:
- Fever
- Rash
- Shortness of breath
- Fast heartbeat.
Water for injection
Brand names: sterile water
Indications:
Water for injection is a form of sterile water used to deliver IV drugs or medications to patients.
Mechanism of action:
- Water for injection is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, solute-free preparation of distilled water.
Side effects: no side effects
2-Pharmaceutical Aids:
Syringes and Needles
Syringes are available in several different designs.
Most are disposable; many come with an attached needle or no needle as needed.
Different sizes and types of syringes are used according to medicine dose and prescription.
Oxygen catheter
An oxygen catheter is a nasal cannula for direct oxygen administration via the nasopharyngeal route.
An oxygen catheter delivers supplemental oxygen to a patient suffering from breathlessness.
Urine catheter
A urinary catheter is a hollow, partially flexible tube that collects urine from the bladder to a drainage bag.
Moreover, urinary catheters come in many sizes and types.
They can be made of rubber, plastic, or silicone.
- A physician recommends urinary catheters if the patient suffers from the following:
- Urinary incontinence
- Urinary retention
- Surgery on the prostate or genitals
- Medical conditions such as spinal cord injury and multiple sclerosis
There are three main types of catheters:
- Indwelling catheter
- Condom catheter
- Intermittent self-catheter
Indwelling catheter
An indwelling urinary catheter is a catheter that is held in the bladder.
An indwelling catheter can be used for a short or long time.
External catheters (condom catheters)
A condom catheter is a condom-like device placed over the penis that leads to a drainage bag.
Sterile suction catheter
- A sterile suction catheter is a small flexible tube used by a respiratory therapist, nurse, or ICU technician for oral suctioning.
- The purpose of oral suctioning is to keep the airways clear of secretions and improve oxygenation.
- A sterile suction catheter removes pharyngeal secretions (mucous secretions, vomit or gastric secretions) from the mouth and throat.
- Mostly used for patients with impaired cough reflex related to age or condition or deficient swallowing patients with respiratory disorders or a high risk of aspiration.
- Also, suction catheters can help clear the airway in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients, especially when they cannot clear secretions independently.
- This prevents the risk of aspiration, pneumonia, and secondary respiratory infections.
Razor suction blades
- Surgical blades are used for making incisions into the skin and tissues.
- At the same time, Razor blades are used for preoperative hair removal needs. Integrated suction helps keep the surgical site clear.
- Benefits of razor suction blades to enhance surgical efficiency and precision when incising or removing soft or hard tissue.
Sterile gelatin sponge
- Sterile gelatin sponge (gel foam) is effective hemostatic gelatin used for stopping intraoperative bleeding rapidly.
- It is water-insoluble, off-white, nonelastic, porous, adheres to the bleeding site, and absorbs approximately 45 times its blood weight.
- Its porous structure activates the thrombocytes. This causes the thrombocytes to promote aggregation, thus acting as a catalyst for fibrin formation, which stops the bleeding.
Resuscitation tube
- A resuscitation tube is a laryngeal tube, a helpful tool for cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is a lifesaving technique useful in many emergencies, such as a heart attack, difficulty breathing, or cardiac arrest.
Oxygen equipment
- Emergency oxygen devices is the Most Important Emergency Drugs and Aids.
- It keep an oxygen supply for aiding people in respiratory or cardiac distress.
- Oxygen devices (compressed gas cylinders, oxygen concentrators, and liquid oxygen) deliver oxygen to patients.
- Emergency oxygen face masks, nasal cannulas, oxygen tubing, and oxygen therapy hoods aid breathing in emergencies and intensive-care settings.
- Medical oxygen equipment delivers and controls the flow of oxygen to patients for providing respiratory therapy for chronic pulmonary diseases and complications of hypoxemia.
Burn sheets
- Burn Sheets are a non-woven tissue fibre that provides emergency first aid for burn victims.
- Burn Sheet 60″ x 90 “, can be folded or in a full-size configuration as an emergency dressing.
- Sterile burn sheets cover the skin of burn victims while being transported to protect the patient from infection.
- Moreover, these sheets wrap the patient completely to protect the patient from contamination and additional trauma until a medical professional arrives to aid.
Surgical instruments like scissors and forceps
- Surgical instruments are used for several purposes by the physician in surgical operations and emergencies.
- Each scissor type serves a different purpose, such as straight operating scissors vs kinesiology scissors.
- Medical forceps are grasping-type surgical tools used during surgical procedures.
Related Articles
- Corticosteroids Common Drug List, Side Effects
- Guidelines of Patient Counseling
- Download Pocket Guide for Antibiotic Pharmacotherapy Book
- Blog of Most Read English Articles
- 10 Skills You Must Learn to Do Research via Google Scholar in Arabic
- FADIC Book store and Buy books in different specialities.

 Log in
Log in Sign up
Sign up