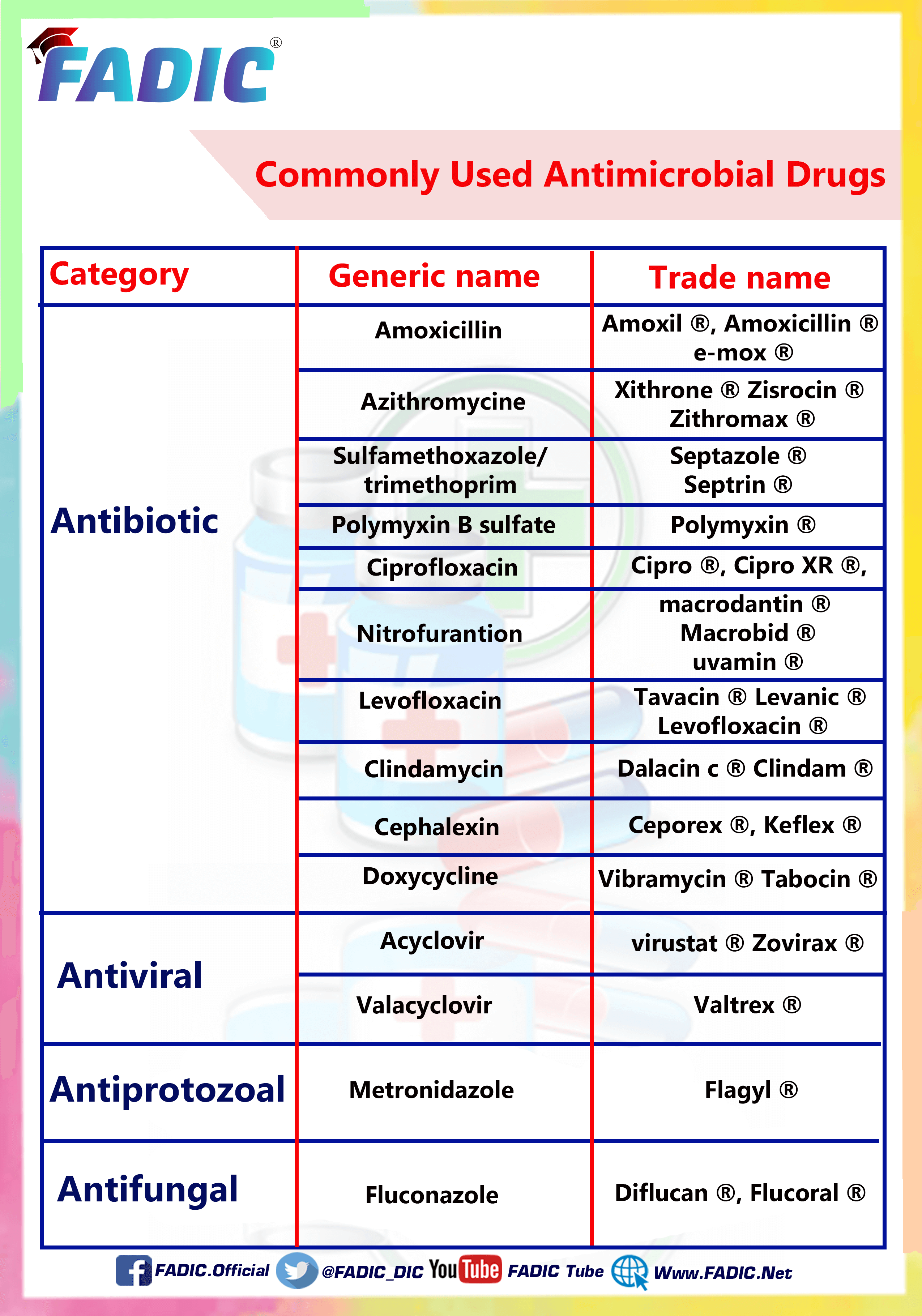
The Most Common Antibiotics are Used in Prescriptions
The Most Common Antibiotics Used in Prescriptions

Within each prescription, there is a drug. Among these drugs, you may find antibiotics…
Antibiotic uses vary and vary, but there are some antibiotics found more common and repeated significantly.
Which called for the need to identify them in more detail and even shed light on them in a summary
In this article, you will read the following ten popular and commonly used Antibiotics:
1- Amoxicillin 💊
2- Azithromycin 💊
3- Cephalexin 💊
4- Ciprofloxacin 💊
5- Clindamycin 💊
6- Doxycycline 💊
7- Levofloxacin 💊
8- Nitrofurantoin 💊
9- Polymyxin B 💊
10- Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim 💊
11- Ceftriaxone 💊
12- Metronidazole 💊
13- Tetracycline 💊
14- Penicillin 💊
15- Ofloxacin 💊
16- Clarithromycin 💊
Amoxicillin
- Brand Names: Moxatag, Emox, Amoxicillin
- Therapeutic Category: Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
- Dosage Forms: oral (Tablet+ Suspension)
- Use: Antibiotics
- Labeled Indications: Ear, nose, and throat infections, Genitourinary tract infections, Lower respiratory tract infections, Skin and skin structure infections, Helicobacter pylori eradication
- Off-Label Indications: Anthrax/ Actinomycosis/ Prophylaxis against bacterial infection in high-risk patients/ Lyme disease /Periodontitis/ Endocarditis, prophylaxis
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: 500 mg to 1 g every 8 to 12 hours
- Geriatric: like adult dosing
- Pediatric: Mild to moderate infection: 25 to 50 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours
Severe infection: 80 to 100 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours.
Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: GFR ≥30 mL/minute: No dosage adjustment necessary.
- GFR 10 to 30 mL/minute: 250 to 500 mg every 12 hours
- GFR <10 mL/minute: 250 to 500 mg every 24 hours
- Hepatic Impairment: Adult: no dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Headache/ Diarrhea / Nausea / Vomiting / Vulvovaginal infection - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Time to peak: Capsule, oral suspension: 1 to 2 hours; Chewable tablet: 1 hour; Extended-release: 3.1 hours
- Half-life elimination: Adults: Immediate-release: 61.3 minutes; Extended-release: 90 minutes
- Excretion: Urine (60% as unchanged drug)
- Important Notes:
- Birth control pills and other hormone-based birth control may not work as well in preventing pregnancy. Use some different types of birth control when taking this drug.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor B/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Amoxicillin may be confused with amoxapine, Augmentin
Amoxil may be confused with amoxapine
Azithromycin
- Brand Names: Zithromax, Zmax, Zicrocin
- Therapeutic Category: Antibiotics, Macrolide
- Dosage Forms: oral (Capsule/ reconstituted susp)/ IV injection
- Use: Antibiotics
- Labeled Indications: Chancroid / Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease / Otitis media, acute / Pneumonia, community-acquired / Skin and skin structure infections/ Streptococcal pharyngitis
- Off-Label Indications: Acne vulgaris/ Bronchiectasis (non-cystic fibrosis), prevention of pulmonary exacerbations/ Campylobacter infection/ Cesarean delivery (intrapartum or after rupture of membranes), preoperative prophylaxis/ Chlamydia trachomatis infection of the pharynx
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: Usual: Immediate release: 500 mg orally as a single dose on day 1, followed by 250 mg orally once a day on days 2 to 5
- Extended-release: 2 g orally once as a single dose
- Parenteral: 500 mg IV once a day as a single dose for at least two days, followed by 500 mg (immediate-release formulation) orally to complete a 7- to 10-day course of therapy
- Geriatric: like adult dosing
- Pediatric: Children ≥6 months: Oral: 10 mg/kg once daily for three days (maximum: 500 mg daily)
Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: Use with caution in patients with GFR <10 mL/minute
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Loose stools/ vomiting/ diarrhea/ Skin rash - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Time to peak: Oral: Oral: Immediate release: 2 to 3 hours; Extended release: 3 to 5 hours
- Half-life elimination: Infants and Children 4 months to 15 years: 54.5 hours
- Adults: Immediate release: 68 to 72 hours; Extended release: 59 hours
- Excretion: Oral, IV: Biliary (major route 50%, unchanged); urine (6% to 14% unchanged)
- Important Notes:
- Tablet may be administered with food to decrease GI effects.
- extended-release suspension (Zmax) is not interchangeable with immediate-r
- Oral suspension, extended-release, should be taken on an empty stomach release formulations
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor B/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Azithromycin may be confused with azathioprine, erythromycin
Zithromax may be confused with Fosamax, Zinacef, Zovirax
Cephalexin
- Brand Names: Daxbia, Keflex, Ceporex
- Therapeutic Category: Beta-Lactam antibiotic (1st generation Cephalosporin)
- Dosage Forms: oral (Tablet or Capsule+ Suspension)
- Use: Antibiotics
- Labeled Indications: Bone infections/ Genitourinary tract infections/ Otitis media/ Respiratory tract infections/ Skin and skin structure infections
- Off-Label Indications: Community-acquired pneumonia/ Endocarditis, prophylaxis/ Prosthetic joint infection
Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: 250 to 1000 mg every 6 hours or 500 mg every 12 hours
- Geriatric: like adult dosing
- Pediatric: 25 to 100 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 6 to 8 hours
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: CrCl 15 to 29 mL/minute: 250 mg every 8 to 12 hours
- CrCl 5 to 14 mL/minute (not yet on dialysis): 250 every 24 hours
- CrCl 1 to 4 mL/minute (not yet on dialysis): 250 mg every 48 to 60 hours
- Hepatic Impairment: Adult: no dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Agitation, confusion, dizziness, fatigue - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Time to peak: 1 hour
- Half-life elimination: Neonates: 5 hours; Children 3-12 months: 2.5 hours; Adults: 0.5 to 1.2 hours (prolonged with renal impairment)
- Excretion: Urine (80% to 100% as unchanged drug) within 8 hours
Important Notes:
- Administer without regard to food.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor B/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Cephalexin may be confused with cefaclor, cefazolin, ciprofloxacin
Keflex may be confused with Keppra, Valtrex
Ciprofloxacin
- Brand Names: Cipro, Cipro XR
- Therapeutic Category: Fluoroquinolone antibiotics
- Dosage Forms: oral/ IV
- Use: Antibiotics
- Labeled Indications: Treatment of complicated urinary tract infections and pyelonephritis due to E. coli/ acute uncomplicated cystitis in female
- Off-Label Indications: Anthrax/ Bite wound infection/ Diabetic foot infections/ bacterial Meningitis / Chancroid/ Endocarditis
Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: the usual dose is 500-750 mg every 12 hours
- Geriatric: like adult dosing
- Pediatric: Not routinely first-line therapy
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: CrCl 10 to 50: Administer 50% to 75% of the usual dose every 12 hours
- CrCl <10 mL/minute: Administer 50% of usual dose every 12 hours.
- Hepatic Impairment: Adult: no dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
– Disabling, tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, and CNS effects. -Increase aortic dissections or ruptures should be avoided in patients at increased risk for developing an aortic aneurysm.
Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Time to peak, serum: Immediate release tablet: 0.5 to 2 hours/ Extended-release tablet: Cipro XR: 1 to 2.5 hours
- Half-life elimination: Children: 4 to 5 hours; Adults: Normal renal function: 3 to 5 hours
- In case of renal function impairment: The half-life is prolonged.
- Important Notes:
- Tablets may be taken without regard to meals
- Avoid concurrent administration of quinolones and antacids as they may decrease the absorption of Quinolones.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
- Ciprofloxacin may be confused with cephalexin
- Cipro may be confused with Ceftin
Clindamycin
- Brand Names: Cleocin, Clindam, Dalacin C
- Therapeutic Category: Antibiotics
- Dosage Forms: oral (Capsule/ reconstituted solution)/ IV.IM injection
- Use:
- Labeled Indications: Bone infections/ Gynecological infections / Intra-abdominal infections / Lower respiratory tract infections/ Skin and skin structure infections
- Off-Label Indications: Acute otitis media / Community-acquired pneumonia / Group B streptococci, maternal prophylaxis for prevention of neonatal disease / Pneumonia due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: Oral: 600 to 1,800 mg/day in 2 to 4 divided doses
IM, IV: 600 to 2,700 mg/day in 2 to 4 divided doses - Geriatric: like adult dosing
- Pediatric: Neonates: IM, IV: 15 to 20 mg/kg/day divided every 6 to 8 hours.
Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Oral:8 to 40 mg/kg/day in 3 to 4 divided doses
IM, IV: 20 to 40 mg/kg/day in 3 to 4 divided doses - Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Metallic taste/ Abdominal pain/ antibiotic-associated colitis/ diarrhea/ vomiting Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Time to peak: Oral: Within 60 minutes; IM: 1 to 3 hours
- Half-life elimination: Neonates: Premature: 8.7 hours, Full-term: 3.6 hours/ Infants 1 month to 1 year: 3 hours/ Children: 2.5 hours/ Adults: 3 hours
- Excretion: Urine (10%) and faeces (3.6%) as active drugs and metabolites
- Important Notes:
- Clindamycin injection contains benzyl alcohol as a preservative, which can cross the placenta and is associated with the potentially fatal “gasping syndrome” in pediatric patients
- It is common to have diarrhoea when taking antibiotics. Rarely a severe form of diarrhoea called Clostridium diff–associated diarrhoea (CDAD) may happen.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor B/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Cleocin may be confused with bleomycin, Clinoril, Cubicin, Lincocin
Clindamycin may be confused with clarithromycin, Claritin, vancomycin, lincomycin
Doxycycline
- Brand Names: Avidoxy, Doxy 100, Vibramycin
- Therapeutic Category: Antibiotic, Tetracycline
- Dosage Forms: oral (Capsule/ reconstituted susp)/ IV injection
- Use: Antibiotics
- Labeled Indications: Acne/ Actinomycosis / Acute intestinal amebiasis/ Clostridium / Gram-negative infections / Gram-positive infections / Sexually transmitted infections
- Off-Label Indications: Cellulitis, mild to moderate/ Surgical prophylaxis, uterine evacuation (induced abortion or pregnancy loss)/ Pelvic inflammatory disease / Rhinosinusitis, acute bacterial
Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: oral: 100 to 200 mg/day in 1 to 2 divided doses
IV: 100 mg every 12 hours. Note: IV form may cause phlebitis. - Geriatric: like adult dosing
- Pediatric: Children >8 years and Adolescents (<45 kg): Oral, IV: 2 to 4 mg/kg/day in 1 to 2 divided doses
Children >8 years and Adolescents (≥45 kg): Oral, IV: Refer to adult dosing.
Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Hypertension/ Anxiety/ Increased lactate dehydrogenase/ Diarrhea/ Nasopharyngitis/ sinusitis - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Time to peak: Immediate release: 1.5 to 4 hours; delayed release: 2.8 to 3 hours
- Half-life elimination: 18 to 22 hours
- Excretion: Feces (30%); urine (23% to 40%)
Important Notes:
- Take on an empty stomach 1 hour or 2 hours after meals.
- Of currently available tetracyclines, doxycycline has the least affinity for calcium
- Pediatric: May cause tissue hyperpigmentation, tooth enamel hypoplasia, or permanent tooth discolouration
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor D/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Doxycycline may be confused with dicyclomine, doxepin, doxylamine
Doxy100 may be confused with Doxil
Vibramycin may be confused with vancomycin, Vibativ.
Levofloxacin
- Brand Names: Levaquin, Levanic, Tavacin
- Therapeutic Category: Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics
- Dosage Forms: oral/ IV
- Use: Antibiotics
- Labeled Indications: Treatment of community-acquired pneumonia, MDR Streptococcus pneumoniae (MDRSP), UTI (uncomplicated or complicated)
- Off-Label Indications: Anthrax/ Diabetic foot infections/ Cervicitis or urethritis due to Chlamydia trachomatis infection/ H.pylori eradication
Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: the usual dose is 500-750 mg every 24 hours
- Geriatric: like adult dosing
- Pediatric: Oral, IV: 10 to 20 mg/kg/day divided every 12 to 24 hours. Recommended in type I penicillin allergy, after the failure of initial therapy o
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: Clearance is reduced; the half-life is prolonged in patients with CrCl less than 50 mL/minute.
- Hepatic Impairment: Adult: no dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
– Common: diarrhoea and insomnia
– Disabling, tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, and CNS effects. - Increase aortic dissections or ruptures should be avoided in patients at increased risk for developing an aortic aneurysm.
- Stopped immediately if a patient reports any blood glucose disturbances; or side effects involving tendons, muscles, or joints.
Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Time to peak, serum: Oral: 1 to 2 hours
- Half-life elimination: Adults: 6 to 8 hours
- In case of renal function impairment: The half-life is prolonged.
- Important Notes:
- Tablets may be taken without regard to meals
- Avoid concurrent administration of quinolones and antacids as they may decrease the absorption of Quinolones.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
- Levaquin may be confused with Levoxyl, Levsin/SL, Lovenox
- LevoFLOXacin may be confused with levETIRAcetam, levodopa, Levophed, or levothyroxine.
Nitrofurantoin
- Brand Names: Furadantin, Macrobid, Macrofuran
- Therapeutic Category: Antibiotic, Miscellaneous
- Dosage Forms: oral capsule/ suspension
- Use: Antibiotics
- Labeled Indications: Acute uncomplicated cystitis, Recurrent cystitis prophylaxis
- Off-Label Indications: None
Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: Nitrofurantoin monohydrate/macrocrystals: Oral: 100 mg twice daily; treat females for five days and males for seven days
Nitrofurantoin microcrystals: oral: 50 to 100 mg every 6 hours; treat females for five days and males for seven days - Geriatric: Avoid use
- Pediatric: Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Nitrofurantoin macrocrystals: Oral: 5 to 7 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 6 hours (maximum: 400 mg daily). Administer for seven days or at least three days after obtaining sterile urine.
- Adolescents: Nitrofurantoin monohydrate/macrocrystals :Oral: 100 mg twice daily for seven days
Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: CrCl ≥60 mL/minute: No dosage adjustments
- CrCl <60 mL/minute: Limited data suggest nitrofurantoin is safe and effective for short-term treatment
- Hepatic Impairment: Adult: no dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
– ECG changes/ Bulging fontanel (infants)/ chills/ confusion/ depression/ dizziness/ drowsiness/ headache/ Alopecia/ erythema multiforme/ exfoliative dermatitis/ pruritus/ skin rash/ Urine discoloration (brown) / Acute pulmonary reaction - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Bioavailability: Increased with food by 40%
- Half-life elimination: 20 to 60 minutes; prolonged with renal impairment
- Excretion: Macrocrystals: Urine (20% to 25% as unchanged drug)
Important Notes:
- Take meals to improve absorption and decrease adverse effects.
- Use caution in patients with G6PD deficiency; they may be at increased risk for hemolytic anaemia. Discontinue therapy if it occurs.
- Avoided in patients 65 years and older (independent of diagnosis or condition) due to its potential for pulmonary toxicity, hepatotoxicity and peripheral neuropathy, particularly when given long-term.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor B (contraindicated at term)/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Macrobid may be confused with micro K, Nitro-Bid.
Nitrofurantoin may be confused with Neurontin and nitroglycerin.
Polymyxin B
- Brand Names: Polymyxin B/ Maxitrol/ Neobacigrin
- Therapeutic Category: Antibiotics, Miscellaneous
- Dosage Forms: Solution Reconstituted, Injection/ ophthalmic drops
- Use: Antibiotics
- Labeled Indications: Infections, acute: Treatment of infections of the urinary tract, meninges, and bloodstream caused by susceptible strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Serious infections: When less potentially toxic drugs are ineffective or contraindicated: H. influenzae, specifically meningeal infections; Escherichia coli, specifically urinary tract infections; Aerobacter aerogenes, specifically bacteremia; Klebsiella pneumonia, specifical bacteremia
- Off-Label Indications: Selective gastrointestinal tract decontamination
Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: Ocular infections: A concentration of 0.1% to 0.25% (10,000 to 25,000 units/mL) is administered as 1 to 3 drops every hour, then increasing the interval as response indicates
- Systemic infections: 15,000 to 25,000 units/kg/day IV divided every 12 hours
- Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing
- Pediatric: Severe, life-threatening, multidrug-resistant infection:
- Dose Adjustments: IV: 15,000 to 40,000 units/kg/day divided every 12 hours (Routine IM administration not recommended due to severe pain at the injection site)
- Renal Impairment: reduce to dose to <15,000 units/kg/day
- Hepatic Impairment: Adult: no dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
- – Neurotoxicity (includes ataxia, blurred vision, drowsiness, irritability, numbness of extremities)/ Urticaria/ Hypocalcemia, hypochloremia, hypokalemia, hyponatremia
Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Time to peak, serum: IM: Within 2 hours
- Half-life elimination: 6 hours, increased with reduced renal function
- Excretion: Urine (<1% as unchanged drug within first 12 hours)
- Important Notes:
- -avoid concurrent or sequential use of other nephrotoxic drugs
- – Avoid concurrent or sequential use of other neurotoxic drugs
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Safety in pregnant women has not been established/ not known if polymyxin b is excreted in human milk
Drug safety issue:
The Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP) includes this medication (intrathecal administration) among its list of drug classes which have a heightened risk of causing significant patient harm when used in error.
Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim
- Brand Names: Bactrim; Bactrim DS, septrin
- Therapeutic Category: Antibiotic, Sulfonamide Derivative
- Dosage Forms: Solution IV/ Oral tablet or suspension
Use: Antibiotics
- Labeled Indications: Treatment of urinary tract infections due to Escherichia coli, Klebsiella and Enterobacter/ treatment and prophylaxis of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP); traveller’s diarrhoea due to enterotoxigenic E. coli.
- Off-Label Indications: Bite wound infections (animal and human bites)/ Brain abscess, empyema, and epidural abscess (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus)/ Diabetic foot infection/ Head lice/ Osteomyelitis
Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: Weight-based dosing recommendations are based on the trimethoprim (TMP) component. Usual 1 to 2 double-strength tablets every 12 to 24 hours
- Geriatric: Refer to adult
- Pediatric: Infants ≥ two months of age, Children, and Adolescents: Oral, IV: 6 to 12 mg TMP/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours
- Renal Impairment: CrCl >30 mL/minute: No dosage adjustment necessary.
- CrCl 15 to 30 mL/minute: Administer 50%
- CrCl <15 mL/minute: Use is not recommended
- Hepatic Impairment: Adult: no dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
– Allergic myocarditis, depression, fatigue, hallucination, headache, insomnia, nervousness, peripheral neuritis, Anaphylaxis, angioedema, hypersensitivity reaction, serum sickness - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Half-life elimination:TMP: Prolonged in renal failure
- Time to peak, serum: Oral: 1 to 4 hours
- Excretion: Both are excreted in urine as metabolites and unchanged drug
Important Notes:
- – Tell your doctor if you have an allergy to sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, or any other part of this drug.
- -shouldn’t be given to infants younger than two months.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: risk factor D/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
- Bactrim may be confused with bacitracin, Bactine, Bactroban
- Co-trimoxazole may be confused with clotrimazole
- Septra may be confused with Ceptaz, Sectral
- Septra DS may be confused with Semprex-D
Ceftriaxone
Brand Names: Ceftriaxone Sandoz
Therapeutic Category: Antibiotic, Cephalosporin (Third Generation)>
Dosage Forms: Solution Reconstituted, Injection
Use: Antibiotic
Labelled Indications:
- Bloodstream infection.
- Bone and joint infections (osteomyelitis and/or discitis, prosthetic joint infection, septic arthritis).
- Gonococcal infection, uncomplicated (cervical/urethral, rectal, and pharyngeal).
- Lower respiratory tract infections (pneumonia, community-acquired).
- Meningitis, bacterial.
- Otitis media, acute.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (mild to moderate).
- Skin and soft tissue infections.
- Surgical prophylaxis, colorectal.
Off-Label Indications:
- Actinomycosis, severe or extensive.
- Bite wound infection, treatment, animal or human bite.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, acute exacerbation (hospitalised patients without risk factors for Pseudomonas aeruginosa).
- Diabetic foot infection.
- Empiric treatment (of sexually transmitted infections) following sexual assault.
Dosing:
Dosing Adult: IV: 1 g once daily for 5 to 7 days.
Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing.
Pediatric: General dosing: Infants, Children, and Adolescents: IM, IV: 50 to 75 mg/kg/dose every 24 hours; maximum dose: 1,000 mg/dose; higher doses are recommended in certain infections (e.g., endocarditis, meningitis)
Dose Adjustments
Renal Impairment:
Altered kidney impairment: IM, IV:
- CrCl >15 mL/minute: No dosage adjustment necessary.
- CrCl <15 mL/minute: No dosage adjustment necessary.
Hepatic Impairment: no dosage adjustments.
Adverse Drug Interaction:
- Ceftriaxone-calcium precipitation
- Clostridioides difficile infection
- Hemolytic anaemia
- Hypersensitivity reactions (immediate and delayed)
- Kernicterus
Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
Time to peak: IM: 2 to 3 hours.
Half-life elimination: Normal renal and hepatic function: 5 to 9 hours.
Excretion: Urine (33% to 67% as unchanged drug); faeces (as inactive drug).
Important Notes:
- Perform culture and sensitivity testing and assess the patient’s allergy history before initiating therapy.
- Obtain renal and liver function tests; dosage adjustments may be needed in patients with concurrent renal and hepatic impairment.
- Obtain PT/INR in patients at risk for elevations.
- Monitor for signs of anaphylaxis during the first dose. Assess for signs of hemolytic anaemia or pancreatitis.
- Hypersensitivity to ceftriaxone, any component of the formulation, or other cephalosporins; do not use in hyperbilirubinemia neonates, particularly those who are premature since ceftriaxone is reported to displace bilirubin from albumin binding sites; concomitant use with intravenous calcium-containing solutions/products in neonates (≤28 days); IV use of ceftriaxone solutions containing lidocaine.
Pregnancy & Lactation:
Category B/ present in breast milk.
Drug safety issue:
CefTRIAXone may be confused with ceFAZolin, cefoTEtan, cefOXitin, cefTAZidime, Cetraxal
Metronidazole
Brand Names: Flagyl
Therapeutic Category: Amebicide, Antibiotic, Miscellaneous
Dosage Forms:
- Capsule, Oral
- Solution, Intravenous
- Solution, Intravenous [preservative-free]
- Tablet, Oral
Use: Amebicide, Antibiotic.
Labelled Indications:
- Amebiasis
- Anaerobic bacterial infections (caused by Bacteroides spp., including the B. fragilis group)
- Surgical prophylaxis (colorectal surgery)
- Trichomoniasis
Off-Label Indications:
- Balantidiasis
- Bite wound infection, prophylaxis or treatment (animal or human bite)
- Clostridioides difficile infection, treatment
- Crohn disease
- Dientamoeba fragilis infection
- Empiric treatment (of sexually transmitted infections) in females following sexual assault
- Giardiasis
Dosing:
Dosing Adult: Oral: 500 to 750 mg every 8 hours for 7 to 10 days.
Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing.
Pediatric:
Infants, Children, and Adolescents:
- Oral: 15 to 50 mg/kg/day in divided doses 3 times daily; maximum daily dose: 2,250 mg/day.
- IV: 22.5 to 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses 3 or 4 times daily; maximum daily dose: 4,000 mg/day.
Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: no dosage adjustments
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustment is necessary; use caution and monitor for adverse events.
Adverse Drug Interaction:
- CNS effects: include peripheral neuropathy, aseptic meningitis, ataxia, neurocerebellar toxicity, confusion or disorientation.
- Disulfiram-like reaction
Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
Time to peak: Oral: 1 to 2 hours
Half-life elimination: Adults: 8 hours
Excretion: Urine
Important Notes:
Prolonged use may result in fungal or bacterial superinfection, including C. difficile-associated diarrhoea (CDAD) and pseudomembranous colitis; CDAD has been observed for>2 months postantibiotic treatment.
Useful as a single agent or combination with amoxicillin, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, or ciprofloxacin in treating periodontitis associated with Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans (AA).
Pregnancy & Lactation:
- Crosses the placenta.
- Present in breast milk
Drug safety issue:
MetroNIDAZOLE may be confused with mebendazole, meropenem, metFORMIN, methotrexate, metoclopramide, miconazole
Tetracycline
Brand Names: Achromycin
Therapeutic Category: Antibiotic, Tetracycline Derivative
Dosage Forms: Capsule, Oral, as hydrochloride
Use: Antibiotic
Labelled Indications:
- Acne
- Actinomycosis
- Anthrax
- Campylobacter
- Cholera
- Clostridium
- Gram-negative infections
Off-Label Indications:
- Helicobacter pylori
- Hidradenitis suppurativa
- Malaria
- Pityriasis lichenoides chronica
- Rosacea
Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: Usual dosage range: Oral: 250 to 500 mg 4 times daily or 500 mg twice daily.
- Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing.
- Pediatric: Children ≥8 years and Adolescents: Oral: 6.25 to 12.5 mg/kg/dose 4 times daily; maximum dose: 500 mg/dose.
Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: no specific dosage adjustments
- Hepatic Impairment: no specific dosage adjustments
Adverse Drug Interaction:
- Cardiovascular: Pericarditis
- Central nervous system: Bulging fontanel, idiopathic intracranial hypertension
- Dermatologic: Erythematous rash, maculopapular rash, skin photosensitivity, urticaria
- Gastrointestinal: Anorexia, diarrhoea, dysphagia
Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Time to peak: Oral: 2 to 4 hours
- Half-life elimination: 6 to 11 hours
- Excretion: Urine (30%); feces (20% to 60%)
Important Notes:
Administer on an empty stomach (i.e., 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals) to increase total absorption and adequate fluid.
Pregnancy & Lactation:
- Crosses the placenta
- Excreted into breast milk
Drug safety issue:
- Tetracycline may be confused with tetradecyl sulfate
Penicillin
Brand Names: Penpro
Therapeutic Category: Antibiotic, Penicillin
Dosage Forms: Suspension, Intramuscular: Generic: 600,000 units/mL (1 mL, 2 mL).
Use: Antibiotic
Labelled Indications:
- Diphtheria: As an adjunct to antitoxin for preventing the carrier stage of diphtheria caused by susceptible Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
- Erysipeloid: Treatment of erysipeloid caused by susceptible Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae.
- Fusospirochetosis: Treatment of fusospirochetosis (Vincent gingivitis and pharyngitis) in conjunction with dental care and moderately severe infections of the oropharynx caused by susceptible fusiform bacilli and spirochetes.
- Pneumococcal infection
Off-Label Indications:
- Anthrax
- Endocarditis
- Staphylococcal infection
Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: Usual dosage range: IM: 600,000 to 1 million units daily; higher doses may be needed for some indications (e.g., diphtheria, neurosyphilis).
- Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing.
- Pediatric: General dosing, susceptible infection (mild to moderate): Infants, Children, and Adolescents: IM: 50,000 units/kg/day in divided doses every 12 to 24 hours; maximum daily dose: 1.2 million units/day.
Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: no dosage adjustments
- Hepatic Impairment: no dosage adjustments
Adverse Drug Interaction:
- Anaphylaxis, central nervous system toxicity, Clostridioides difficile colitis, exfoliative dermatitis, hypersensitivity reaction, Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction, maculopapular rash, serum sickness-like reaction, skin rash, urticarial.
Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Time to peak: Within 1 to 4 hours
- Excretion: Urine (60% to 90% as unchanged drug)
Important Notes:
- Serious and occasionally severe or fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported in patients on penicillin therapy
Pregnancy & Lactation:
- Crosses the placenta.
- Present in breast milk.
Drug safety issue:
- Penicillin may be confused with penicillamine
- Penicillin G procaine may be confused with penicillin V potassium
Ofloxacin
Brand Names: Avaflox, Akilen.
Therapeutic Category: Antibiotic, Fluoroquinolone
Dosage Forms: tablet 200mg, 300mg, 400mg.
Use: Antibiotic
Labelled Indications:
Treatment of community-acquired pneumonia, skin and soft tissue infections (uncomplicated), urethritis and cervicitis (nongonococcal) due to Chlamydia trachomatis infection, pelvic inflammatory disease (acute), cystitis (uncomplicated), urinary tract infections (complicated), prostatitis.
Off-Label Indications:
- Epididymitis, acute
- Traveler’s diarrhoea
Dosing:
Dosing Adult:
- Epididymitis, acute : Oral: 200 mg twice daily for 14 days.
- Pneumonia, community-acquired: Oral: 400 mg every 12 hours.
- Prostatitis: Oral: 300 mg every 12 hours for six weeks.
Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing.
Pediatric: Children: Oral: 15 mg/kg/day divided every 12 hours.
Dose Adjustments
Renal Impairment: Oral: After a normal initial dose, adjust as follows:
- CrCl >50 mL/minute: No dosage adjustment necessary.
- CrCl 20 to 50 mL/minute: Administer the usual recommended dose every 24 hours.
- CrCl <20 mL/minute: Administer half the usual recommended dose every 24 hours.
Hepatic Impairment:
- Mild to moderate impairment: no dosage adjustments
- Severe impairment (e.g., cirrhosis with or without ascites): Maximum dose: 400 mg/day
Adverse Drug Interaction:
- Cardiovascular: Chest pain
- Central nervous system: Headache, insomnia, dizziness, fatigue, drowsiness, sleep disorder.
- Dermatologic: Pruritus, skin rash, genital pruritus
- Gastrointestinal: Nausea, diarrhoea, vomiting
Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Time to peak: 1 to 2 hours.
- Half-life elimination: 9 hours
- Excretion: Urine: 65% to 80% (as unchanged drug)
Important Notes:
Fluoroquinolones have been associated with disabling and potentially irreversible severe adverse reactions that have occurred together, including tendinitis and tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, and CNS effects. Discontinue ofloxacin immediately and avoid the use of fluoroquinolones in patients who experience any of these severe adverse reactions.
Pregnancy & Lactation:
- Crosses the placenta
- Excreted in breast milk
Clarithromycin
Brand Names: ACT Clarithromycin XL, APO-Clarithromycin
Therapeutic Category: Antibiotic, Macrolide
Dosage Forms:
- Suspension Reconstituted, Oral
- Tablet, Oral
- Tablet Extended Release 24-Hour, Oral
Use: Antibiotic
Labelled Indications:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, acute exacerbation.
- Helicobacter pylori eradication.
- Mycobacterial (nontuberculous) infection.
- Otitis media.
- Pneumonia, community-acquired.
Off-Label Indications:
- Bartonella spp. infection
- Bronchiolitis obliterans, including diffuse panbronchiolitis and symptomatic cryptogenic bronchiolitis obliterans
- Endocarditis, prophylaxis, dental or invasive respiratory tract procedure
- Mycobacterial (nontuberculous, rapidly growing) infection.
- Pertussis
Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: IR and ER formulations are available; 500 mg every 12 hours of immediate release is equivalent to 1 g of extended-release (two 500 mg ER tablets) once daily.
- Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing.
- Pediatric: Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Oral: 7.5 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours; maximum dose: 500 mg/dose
Dose Adjustments
Renal Impairment:
- CrCl <30 mL/minute: IR: 250 mg once daily
- Intermittent hemodialysis, thrice weekly: IR: 250 mg once daily.
Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustment
Adverse Drug Interaction:
- Central nervous system: Headache, insomnia
- Dermatologic: Skin rash
- Gastrointestinal: Dysgeusia, vomiting, diarrhoea, nausea, abdominal pain, dyspepsia
- Hematologic & oncologic: Prolonged prothrombin time
- Hepatic: Abnormal hepatic function tests
- Hypersensitivity: Anaphylactoid reaction
Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Time to peak: Immediate release: 2-3 hours; Extended release: 5-8 hours
- Half-life elimination: 3-7 hours
- Excretion: Urine
Important Notes:
- Use has been associated with QT prolongation and infrequent cases of arrhythmias, including torsades de pointes (may be fatal); avoid use in patients with known prolongation of the QT interval, ventricular cardiac arrhythmia.
- Elevated liver function tests and hepatitis have been reported, usually reversible after discontinuation of clarithromycin.
Pregnancy & Lactation:
- Crosses the placenta, present in breast milk.
Drug safety issue:
- Clarithromycin may be confused with Claritin, clindamycin, erythromycin
Read More:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship School
- Sepsis Training Program
- Download Pocket Guide for Antibiotic Pharmacotherapy Book
- Microbiology Course | ABC Bacteria
- Infectious Disease E-News | FREE Subscription
- ABC antimicrobials | Know all about the Antimicrobials
- Road Map to Antimicrobial Stewardship Training Program
- Register Now in FADIC Clinical Research School
- FADIC Drug Information Fellowship
- Buy FADIC Toolkit for Writing Research to Write a Great Research Paper
- Read 10 Skills You Must Learn to Do Research via Google Scholar in Arabic
- The FADIC Online Continuous Medical Improvement Programs & Mini-Courses.
- Check Now FADIC Book store and Buy books in different specialities.
- Watch Now FADIC TV to Keep Yourself Updated.
- FADIC Podcast focuses on varieties of pharmacist perspectives in different specialities.
- Subscribe Now to FADIC 2020 Daily News (FNN) and Keep Updated.
- Check Now about Coronavirus Resource Information Center.
- Download Now The Antibiotic Cards Book

 Log in
Log in Sign up
Sign up




