The Most Common Asthma Medications: Inhalers, Nebulizers
The Most Famous 5 drugs most Commonly used as Asthma Inhalers are:
1- Albuterol💊
2- Budesonide and Formoterol 💊
3- Fluticasone and Salmeterol 💊
4- Ipratropium and Albuterol 💊
5- Tiotropium 💊
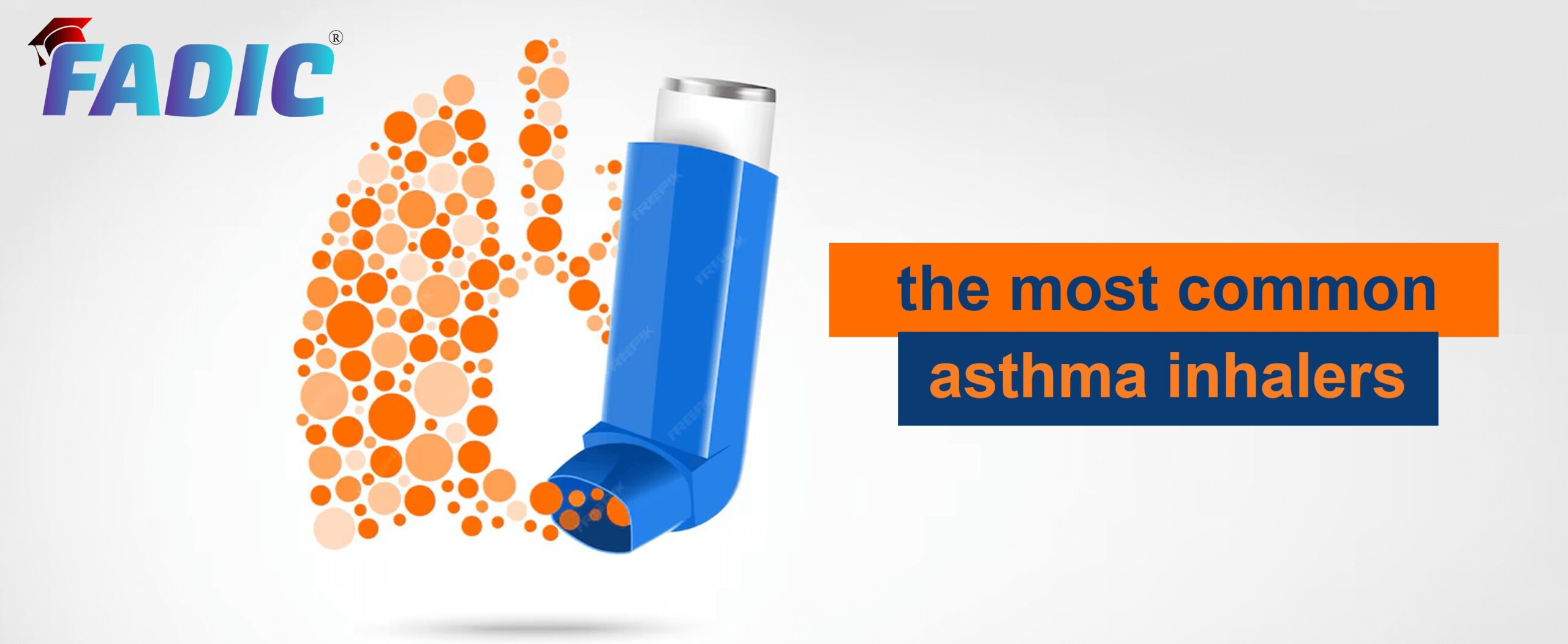
Albuterol
- Brand Names: Ventolin
- Therapeutic Category: Beta2 Agonist used as Asthma Medications
- Dosage Forms: Aerosol Powder, Inhalation/ Nebulization Solution, Inhalation/ Oral syrup, tablet
- Use: Labeled Indications: Bronchospasm/ Exercise-induced bronchospasm
- Off Label: Hyperkalemia
- Dosing : Bronchospasm: Oral inhalation :Metered-dose inhaler (MDI) or dry powder inhaler (90 mcg/actuation): 2 inhalations every 4 to 6 hours as needed
- Pediatric: Asthma, acute exacerbation: Infants and Children ≤5 years:
- Metered-dose inhaler: 90 mcg/actuation: Oral inhalation: 2 to 6 inhalations every 20 minutes for 2 to 3 doses, if initial response to 2 doses is good, administer 2 to 6 inhalations every 3 to 4 hours for 24 to 48 hours
- Children ≥6 years and Adolescents: Metered-dose inhaler: 90 mcg/actuation: Oral inhalation: 2 to 10 inhalations every 20 minutes for 2 to 3 doses during the first hour ,if initial response to 2 doses is good, administer 2 to 6 inhalations every 3 to 4 hours for 24 to 48 hours
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Excitement/ nervousness/ Tremor/ Upper respiratory tract infection/ rhinitis - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Half-life elimination: Oral inhalation: 3.8 to 5 hours
- Time to peak, serum: Nebulization solution: 30 minutes
- Onset of action: Nebulization solution: ≤5 minutes
- Important Notes:
- CNS stimulation, hyperactivity, and insomnia occur more frequently in younger children than in adults. In children receiving oral albuterol therapy
- Pregnancy & Lactation: crosses the placenta / not known if present in breast milk
- Medication Safety Issues:
Salbutamol may be confused with salmeterol
Ventolin may be confused with phentolamine, Benylin, Vantin
Highly recommend online Marketing tool from SEMRUSH
Budesonide and Formoterol
- Brand Names: Symbicort
- Therapeutic Category: Beta2 Agonist/ Corticosteroid
- Dosage Forms: oral Inhalation
- Use: Labeled Indications: Asthma Medications/ Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Off-Label: Asthma, acute exacerbations
- Dosing: Asthma (maintenance): Oral inhalation: Starting dose is based on asthma severity. Budesonide 80 mcg/formoterol 4.5 mcg or budesonide 160 mcg/formoterol 4.5 mcg: Metered-dose inhaler: 2 inhalations twice daily; if response is inadequate, may increase to higher dose combination after 1 to 2 weeks (maximum: budesonide 160 mcg/formoterol 4.5 mcg: 2 inhalations twice daily).
- Pediatric: Asthma; maintenance treatment: Oral inhalation: Children 5 to 11 years: Budesonide 80 mcg/formoterol 4.5 mcg: Two inhalations twice daily; maximum daily dose: 4 inhalations (Budesonide 320 mcg/formoterol 18 mcg)/day
- Children ≥12 years and Adolescents:
- Budesonide 80 mcg/formoterol 4.5 mcg: Two inhalations twice daily; maximum daily dose: 4 inhalations (Budesonide 320 mcg/formoterol 18 mcg)/day. In patients not adequately controlled following 1 to 2 weeks of therapy, consider the higher dose combination. Budesonide 160 mcg/formoterol 4.5 mcg: Two inhalations twice daily; maximum daily dose: 4 inhalations (Budesonide 640 mcg/formoterol 18 mcg)/day
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Headache/ Upper respiratory tract infection / Nasopharyngitis - Important Notes:
- Adrenal suppression: Fluticasone may cause hypercortisolism or suppression of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis in sensitive patients.
- Asthma-related deaths: The use of long-acting beta-2 agonists (LABAs) as monotherapy is associated with an increased risk of asthma-related deaths.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Adverse events were observed in animal reproduction studies / not known if present in breast milk
Fluticasone and Salmetero
- Brand Names: Advair Diskus
- Therapeutic Category: Beta2 Agonist/ Corticosteroid
- Dosage Forms: oral Inhalation
- Use: Labeled Indications: Asthma Medications/ Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Dosing : Asthma: Advair Diskus: Dry powder inhaler: Initial: 1 inhalation of fluticasone propionate 100 mcg/salmeterol 50 mcg, or fluticasone propionate 250 mcg/salmeterol 50 mcg, or fluticasone propionate 500 mcg/salmeterol 50 mcg twice daily (maximum dose: 1 inhalation of fluticasone propionate 500 mcg/salmeterol 50 mcg twice daily)
- Pediatric: Children 4 to 11 years: Fluticasone propionate 100 mcg/salmeterol 50 mcg: Oral inhalation: 1 inhalation twice daily.
- Children ≥12 years and Adolescents: Oral inhalation:
- The Fluticasone propionate 100 mcg/salmeterol 50 mcg: 1 inhalation twice daily.
- In addition to, Fluticasone propionate 250 mcg/salmeterol 50 mcg: 1 inhalation twice daily.
- Fluticasone propionate 500 mcg/salmeterol 50 mcg: 1 inhalation twice daily.
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Headache/ Upper respiratory tract infection /pneumonia/ Cardiac arrhythmia - Important Notes:
- Adrenal suppression: Fluticasone may cause hypercortisolism or suppression of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis in sensitive patients.
- Asthma-related deaths: The use of long-acting beta-2 agonists (LABAs) as monotherapy is associated with an increased risk of asthma-related deaths.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Adverse events were observed in animal reproduction studies / not known if present in breast milk
- Medication Safety Issues: Advair may be confused with Adcirca, Advicor
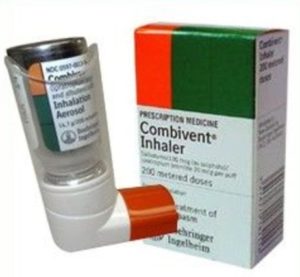
Ipratropium and Albuterol
- Brand Names: Combivent Respimat
- Therapeutic Category: Anticholinergic Agent/ Beta2 Agonist
- Dosage Forms: Solution, for nebulization/ inhalation
- Use: Labeled Indications: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Off-Label: Asthma, acute exacerbations
- Dosing: COPD: Oral inhalation: Soft-mist inhaler: One inhalation 4 times daily (maximum: 6 inhalations/day)
- Nebulization solution: Initial: 1 vial (3 mL) (ipratropium bromide 0.5 mg/albuterol 2.5 mg) every 6 hours (maximum: 6 vials [18 mL]/day)
- Pediatric: Infants and Children: Nebulization solution (ipratropium bromide 0.5 mg/albuterol 2.5 mg): Oral inhalation: 1.5 to 3 mL every 20 minutes for 3 doses, then as needed for up to 3 hours.
- Adolescents: Nebulization solution (ipratropium bromide 0.5 mg/albuterol 2.5 mg): Oral inhalation: 3 mL every 20 minutes for 3 doses, then as needed for up to 3 hours.
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Angina pectoris/ cardiac arrhythmia/ Headache / pain / dizziness / fatigue / insomnia - Important Notes:
- Bronchospasm: Paradoxical bronchospasm that may be life-threatening may occur with use of inhaled bronchodilating agents.
- CNS effects: May cause dizziness and blurred vision; patients must be cautioned about performing tasks which require mental alertness (eg, operating machinery or driving)
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ not known if present in breast milk.
- Medication Safety Issues:
- DuoNeb may be confused with DuoTrav, Duovent UDV
Tiotropium
- Brand Names: Spiriva
- Therapeutic Category: Anticholinergic Agent
- Dosage Forms: inhalation (Aerosol Solution/ Capsule)
- Use: Labeled Indications: Asthma Medications/ Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Dosing: Asthma: Oral inhalation: Spiriva Respimat (1.25 mcg/actuation): Soft-mist inhaler: Two inhalations (2.5 mcg) once daily (maximum: 2 inhalations per 24 hours).
- Pediatric: Asthma: Children ≥6 years of age and Adolescents: Inhalation: Spiriva Respimat (1.25 mcg/actuation)
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Xerostomia/ Upper respiratory tract infection / pharyngitis /sinusitis - Pharmacodynamics:
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Bioavailability: Following inhalation, 19.5% (dry powder inhaler) or ~33% (soft-mist inhaler)
- Time to peak, plasma:Dry powder inhaler: 7 minutes
- Important Notes:
- Bronchospasm: Paradoxical bronchospasm may occur with use of inhaled agents; discontinue use and consider other therapy if bronchospasm occurs.
- CNS effects: May cause dizziness and blurred vision; patients must be cautioned about performing tasks that require mental alertness (eg, operating machinery or driving).
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Adverse events have been observed in animal reproduction studies/ not known if present in breast milk.
- Medication Safety Issues:
Spiriva may be confused with Apidra, Inspra, Serevent
Tiotropium may be confused with ipratropium
Read More:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship School
- Sepsis Training Program
- Download Pocket Guide for Antibiotic Pharmacotherapy Book
- Microbiology Course | ABC Bacteria
- Infectious Disease E-News | FREE Subscription
- ABC antimicrobials | Know all about the Antimicrobials
- Road Map to Antimicrobial Stewardship Training Program
- Register Now in FADIC Clinical Research School
- FADIC Drug Information Fellowship
- Buy FADIC Toolkit for Writing Research to Write a Great Research Paper
- Read 10 Skills You Must Learn to Make a Research via Google Scholar in Arabic
- The FADIC Online Continuous Medical Improvement Programs & Mini-Courses.
- Check Now FADIC Book store and Buy books in different specialties.
- Watch Now FADIC TV to Keep your self Updated.
- FADIC Podcast focusing on varieties of pharmacist perspectives in different specialties.
- Subscribe Now in FADIC 2020 Daily News (FNN) and Keep Updated.
- Check Now about Coronavirus Resource Information Center.
- Read about Asthma Medications

 Log in
Log in Sign up
Sign up