The Most Common OTC Resource
The Most Common OTC Resource
Navigating Over-the-Counter Choices
The Indispensable Guidance of Pharmacists
What are Over the Counter (OTC) Medications?
- OTC drugs are medications that are deemed safe and effective for use by the general public without seeking treatment from a health professional.
- People can follow the “Drug Facts Label” directions on OTC products for proper use.
- OTC medicines treat various symptoms due to illness, including pain, coughs and colds, diarrhoea, heartburn, constipation, acne, and fungal infections. These drugs are usually located on shelves in pharmacies, grocery stores, gas stations and even online.
Famous examples include
- pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB).
- Cough suppressants such as dextromethorphan (Robitussin).
- Antihistamines like loratadine (Claritin 24H)
- Since the use of OTC products has increased for all major therapeutic categories, education about the proper use of OTC products is essential.
- Because the number of OTC products on the market continues to expand, selecting these products may be overwhelming for many patients.
- According to the American Pharmacists Association, of the 3.5 billion health problems treated yearly, an estimated 2 billion are treated with OTC products. The Most Common OTC Resource
What Is the Most Commonly Used OTC Medication?
The most commonly used over-the-counter medications include:
- Pain relievers such as acetaminophen, aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen.
- Medicines for heartburn and indigestion include omeprazole, lansoprazole, cimetidine, and aluminium hydroxide.
- Laxatives such as bisacodyl and calcium docusate.
- Antidiarrheal drugs such as bismuth subsalicylate and loperamide.
- Motion sickness medicines such as dimenhydrinate.
- Nasal steroids such as fluticasone and triamcinolone.
- Cough medicines such as guaifenesin.
- Antihistamines such as fexofenadine and loratadine.
- Emollients and mild corticosteroid creams.
What Are the Most Common resource?
The ten most common over-the-counter medicines used worldwide include:
- Acetaminophen
- Ibuprofen
- Fexofenadine
- Loratadine
- Hydrocortisone creams
- Dextromethorphan
- Pseudoephedrine
- Bismuth subsalicylate
- Diphenhydramine
- Pseudoephedrine
What Are the 3 Most Abused Over-the-counter Drugs?
Certain active ingredients in over-the-counter medicines have the potential for abuse if taken more than the recommended dose, and these include:
Pseudoephedrine is used in cold medicines and can cause the following side effects if abused:
- Dilated pupils
- Hallucinations
- Hypertension
- Heart arrhythmias
- Seizures
- Skin reactions
Dextromethorphan is used as a cough suppressant. Symptoms of dextromethorphan abuse include:
- Lack of energy
- Hyperexcitability
- Poor motor control
- Stomach pain
- Increased blood pressure
- Vision changes
- Slurred speech
- Sweating
Loperamide used as an antidiarrheal can cause the following side effects if misused:
- Fainting
- Stomach pain
- Constipation
- Eye changes
- Loss of consciousness
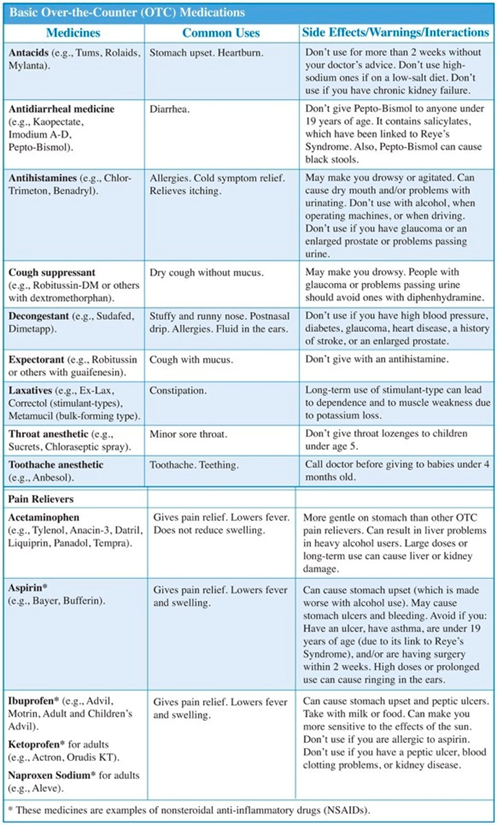
As the number of OTC drugs on the market continues to increase, and as the FDA approves more prescription drugs to nonprescription status, the potential for drug interactions also increases.
Therefore, patients must consult pharmacists to become educated about the appropriate use of these products.
Pharmacists can provide patients with the necessary information to make proper selections when choosing OTC products. They can encourage them to read the labels of OTC products thoroughly and always ask questions if they are uncertain about their choice and proper use.
The Role of Pharmacist in Proper Over-the-Counter (OTC) Product Selection
- The role of a pharmacist in proper over-the-counter (OTC) product selection is crucial to ensuring the safety and efficacy of these products for consumers.
- Pharmacists are highly trained healthcare professionals who deeply understand medications and their effects on the body.
- They play a pivotal role in guiding patients in selecting the most suitable OTC products for their specific health needs.
Here are among several reasons why the role of a pharmacist in OTC product selection is essential:
- Expertise in medication management: Pharmacists are well-versed in the mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, and drug interactions of various medications.
They possess the necessary knowledge to evaluate the appropriateness of OTC products based on an individual’s medical history, medications, and specific symptoms.
This expertise allows them to identify potential risks and recommend the most suitable OTC product. - Understanding of the healthcare system: Pharmacists often comprehensively understand the local healthcare system, including the various healthcare providers and available resources.
They can help patients determine whether their symptoms can be safely managed with an OTC product or if they need to seek further medical attention. one of The Most Common OTC Resource
This guidance ensures that patients receive appropriate care and avoid unnecessary healthcare costs. - Individualized counselling: Pharmacists can engage in one-on-one counselling sessions with patients.
This personalized approach allows them to gather detailed information about a patient’s condition. It provides an opportunity to educate patients about their symptoms, treatment options, and the proper use of OTC products.
This counselling helps patients choose the right OTC product, improves their understanding of their condition, and promotes medication adherence. The Most Common OTC Resource - Preventing adverse effects and drug interactions: OTC products may have potential side effects and interactions with other medications, supplements, or medical conditions.
Pharmacists are trained to identify these risks and provide appropriate recommendations to minimize adverse effects. They can also assess if the symptoms may be masked using an OTC product, which could delay proper diagnosis and treatment. - Access to evidence-based information: Pharmacists have access to various resources, such as drug databases, clinical guidelines, and scientific literature, which provide them with evidence-based information to support their recommendations.
They can stay updated on the latest product recalls, safety warnings, and advancements in OTC products, ensuring they can provide patients with the most up-to-date and accurate information. - Patient advocacy: Pharmacists advocate for their patients’ health and well-being.
- Optimizing therapeutic outcomes: Pharmacists recommend OTC products and provide proper guidance on their correct usage and dosage.
They educate customers about potential side effects, duration of use, and when to seek medical advice.
By doing so, pharmacists ensure that customers achieve the desired therapeutic outcomes and minimize the risk of misuse or adverse effects. The Most Common OTC Resource. - Monitoring and follow-up: If a customer has already been on a particular OTC product, pharmacists can monitor their progress and evaluate its effectiveness.
If necessary, they can suggest adjustments, alternative products, or referral to a healthcare professional. This follow-up process ensures customers receive the most appropriate care and get the best possible results.
Overall, pharmacists are essential as OTC product selector experts because they possess the knowledge, skills, and ability to assess individual needs, recommend suitable products, identify potential risks, and optimize therapeutic outcomes. Their expertise contributes to OTC products’ safe and effective use, promoting better customer health outcomes.
The Role of the Pharmacist in the Use of OTC Drugs

- While more is being done to promote awareness regarding the importance of the safety and appropriate use of OTC drugs, pharmacists are still the patient’s best resource in properly selecting OTC products.
- Moreover, while it is essential for all patients to properly use OTC products, individuals of advanced age, individuals with pre-existing medical conditions such as diabetes, the pediatric population, and those currently using prescription drugs should always consult a healthcare professional when considering the use of OTC drugs to avoid possible contraindications, drug-drug interactions, food-drug interactions, and dosing errors. The Most Common OTC Resource.
- In assisting patients in selecting OTC products, pharmacists should assess the patient’s symptoms/condition to determine if self-treatment is appropriate or if medical treatment is warranted and evaluate for potential allergies.
- When patients are taking multiple OTC products, pharmacists should encourage patients always to check the active ingredients of these products and ensure that a particular element is not in another product they are taking to avoid possible over-dosages and to use only products that treat their specific symptoms and therefore avoid the unnecessary use of multiple products.
How Do You Maintain the OTC Evidence-Based Prescribing?
- OTC (Over-the-Counter) evidence-based prescribing refers to recommending and prescribing available medications without a prescription based on scientific evidence and proven effectiveness.
- Maintaining OTC (over-the-counter) evidence-based prescribing involves following several key steps:
- Stay current with current evidence: Keep yourself updated with the latest research, guidelines, and recommendations related to OTC medications. This can be done through medical journals, reputable websites, and continuing education programs.
- Assess the evidence: Evaluate the quality and relevance of the available evidence. Look for studies demonstrating the effectiveness, safety, and appropriate use of OTC medications for specific conditions or symptoms.
- Consider patient factors: Individual characteristics such as age, medical history, current medications, allergies, and potential drug interactions. This information will help you determine whether OTC medications suit a particular patient.
- Educate patients: Provide accurate and evidence-based information about OTC medications, including indications, contraindications, potential side effects, and proper use. Please encourage them to read and follow product labels and seek professional advice when necessary.
- Promote self-care: Empower patients to make informed decisions about their health by supporting self-care practices. Encourage appropriate self-medication and educate patients about when it is essential to seek professional advice or escalate to prescription medications.
- Collaborate with colleagues: Consult with other healthcare professionals, such as pharmacists, when needed. Pharmacists can provide valuable insights regarding OTC medications, including potential interactions and appropriate dosing regimens.
- Monitor outcomes: Follow up with patients to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of OTC medications. If symptoms persist or worsen, reevaluate the treatment plan, consider other options or involve a healthcare professional if necessary.
- Adhere to ethical guidelines and regulatory requirements: Always practice within your professional standards and adhere to local laws and regulations related to OTC medications.
In conclusion, OTC evidence-based prescribing is crucial in ensuring patient access to adequate and affordable healthcare options. It empowers patients, reduces healthcare costs, and helps manage healthcare resources efficiently. By following evidence-based guidelines, healthcare professionals can confidently recommend OTC medications, knowing that they provide safe and effective treatment options to their patients. The Most Common OTC Resource
Conclusion
- OTC drugs are medications that are deemed safe and effective for use by the general public without seeking treatment from a health professional. The Most Common OTC Resource.
- In an age of self-diagnosis and information overload, the pharmacist’s role remains indispensable, offering reassurance and expertise to those seeking the best over-the-counter solutions.
- OTC aisle can be overwhelming, with many choices promising relief for many ailments. Pharmacists must sift through this complexity, applying their deep understanding of medications, their potential side effects, and their interactions with other drugs. The Most Common OTC Resource
Read More:
- 10 Skills You Must Learn to Do Research via Google ScholarThe Most Common OTC Resource
- Register Now at FADIC Clinical Research School
- Buy FADIC Toolkit for Writing Research to Write a Great Research PaperThe Most Common OTC Resource
- Read 10 Skills You Must Learn to Do Research via Google Scholar in Arabic
- The FADIC Online Continuous Medical Improvement Programs & Mini-Courses.The Most Common OTC Resource
- Check Now the FADIC Book store and Buy books in different specialities.
- Check Now about Coronavirus Resource Information Center.The Most Common OTC Resource
- Simple random sampling: Definition, examples, and how to do itThe Most Common OTC Resource

 Log in
Log in Sign up
Sign up
