Proton Pump Inhibitors
Proton Pump Inhibitors
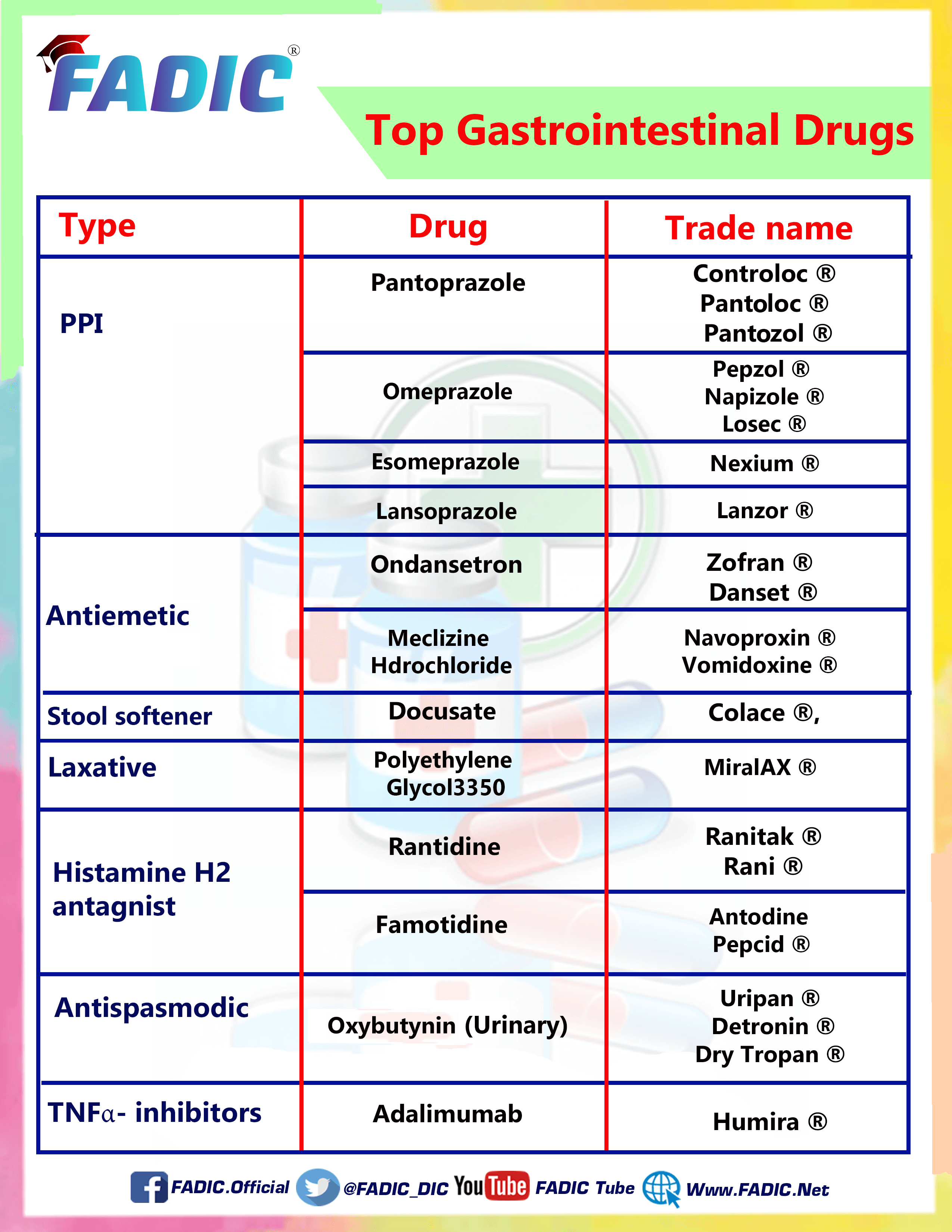
The Most Famous 4 drugs for Proton Pump Inhibitors are:
1- Omeprazole 💊
2- Pantoprazole 💊
3- Esomeprazole 💊
4- Lansoprazole 💊
Omeprazole
- Brand Names: Losec
- Therapeutic Category: Proton Pump Inhibitors
- Dosage Forms: Oral Capsule/ Tablet
- Use: Labeled Indications: Duodenal ulcer, Gastric ulcer, Gastroesophageal reflux disease, Heartburn, Helicobacter pylori eradication
- Off-Label: Dyspepsia, NSAID-induced ulcer treatment, NSAID-induced ulcer prophylaxis, Stress ulcer prophylaxis in critically ill patients
- Dosing : Adult: Duodenal ulcer: Oral: 20 mg once daily for 4 weeks; some patients may require an additional 4 weeks.
- Gastric ulcers: Oral: 40 mg once daily for 4 to 8 weeks
- Pediatric : Erosive esophagitis, treatment (short-term): Oral: Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Duration of therapy for infants is up to 6 weeks. The duration of therapy for children and adolescents is 4 to 8 weeks.
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment:. No dosage adjustment.
- Hepatic Impairment: Mild to severe impairment: 10 mg once daily when used for maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Headache/ Abdominal pain/ diarrhea/ flatulence/ vomiting - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 1 hour
- Time to peak: 0.5 to 3.5 hours
- Duration: Up to 72 hours
- Half-life elimination: 0.5 to 1 hour; hepatic impairment: 3 hours
- Important Notes:
- Use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) may increase risk of CDAD(Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea ) , especially in hospitalized patients
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Available data have not shown an increased risk of major birth defects/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Omeprazole may be confused with aripiprazole, esomeprazole, fomepizole
PriLOSEC may be confused with Plendil, Prevacid, predniSONE, prilocaine
Pantoprazole
- Brand Names: Protonix
- Therapeutic Category: Proton Pump Inhibitors
- Dosage Forms: Oral /Tablet/ Packet , IV solution Reconstituted
- Use: Labeled Indications: Erosive esophagitis associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease, Maintenance of healing of erosive esophagitis, Pathological hypersecretory conditions, including Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
- Off-Label: DyspepsiaLevel of Evidence ,Helicobacter pylori eradicationLevel of Evidence, Prevention of NSAID-induced ulcersLevel of Evidence, Prevention of rebleeding in peptic ulcer bleed
- Dosing : Adult: Dyspepsia: Oral: 20 to 40 mg once daily for 4 weeks
- Erosive esophagitis associated with GERD:Oral: 40 mg once daily for up to 8 weeks; an additional 8 weeks may be used in patients who have not healed after an 8-week course
- Pediatric : Children 5 to 11 years: Oral: 20 or 40 mg once daily have been shown to reduce severity and frequency of symptoms within 1 week Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment:. No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Dizziness, vertigo, headache, Facial edema - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: Acid secretion: Oral: 2.5 hours
- Time to peak: 2.5 hours
- Bioavailability: 77%
- Half-life elimination: 1 hour
- Important Notes:
- Use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) may increase risk of CDAD(Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea ) , especially in hospitalized patients
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Recommendations for the treatment of GERD in pregnancy are available / present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Pantoprazole may be confused with ARIPiprazole
Protonix may be confused with Lotronex, Lovenox, protamine
Esomeprazole
- Brand Names: Nexium
- Therapeutic Category: Proton Pump Inhibitors
- Dosage Forms: Oral Capsule/Tablet/ Packet , IV solution Reconstituted
- Use: Labeled Indications: Short-term treatment (up to 6 weeks) of erosive esophagitis associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- short-term treatment (4 to 8 weeks) and maintenance of healing of severe erosive esophagitis
- Adjunctive treatment of duodenal ulcers associated with Helicobacter pylori
- Dosing : Adult: Erosive esophagitis: Initial: 20 to 40 mg once daily for 4 to 8 weeks; if incomplete healing, may continue for an additional 4 to 8 weeks
- Dyspepsia (off-label use): Oral: 40 mg once daily for up to 8 weeks
- Pediatric : Neonatal: Oral: 0.5 mg/kg/dose given once daily for 7 days
- 3 to 5 kg: 2.5 mg once daily for up to 6 weeks
- >5 to 7.5 kg: 5 mg once daily for up to 6 weeks
- >7.5 kg: 10 mg once daily for up to 6 weeks
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment:. Severe impairment: Use is not recommended
- Hepatic Impairment: Severe impairment: 20 mg once daily
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Esophageal varices, Dizziness, drowsiness, headache, irritability - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 1 to 3 hours
- Time to peak: 1.5 to 2 hours
- Bioavailability: Oral: 64 after a single dose
- Half-life elimination: 1 to 1.5 hours
- Important Notes:
- Use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) may increase risk of CDAD(Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea ) , especially in hospitalized patients
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Recommendations for the treatment of GERD in pregnancy are available / present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Esomeprazole may be confused with ARIPiprazole, omeprazole
NexIUM may be confused with NexAVAR
Lansoprazole
- Brand Names: Prevacid
- Therapeutic Category: Proton Pump Inhibitors
- Dosage Forms: Oral Capsule/ Tablet Disintegrating
- Use: Labeled Indications: Gastroesophageal reflux disease, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, Peptic ulcer disease
- Off-Label: Dyspepsia, Stress ulcer prophylaxis in critically-ill patients
- Dosing : Adult: Administer 30 to 60 minutes before a meal
- Mild and intermittent symptoms: 15 mg once daily for 8 weeks; if symptoms persist after 8 weeks, increase to 30 mg once daily
- Severe or frequent symptoms: Oral: 30 mg once daily; once symptoms are controlled, continue treatment for at least 8 weeks
- Pediatric : Infants: 1 to 2 mg/kg/day
- Children: 0.7 to 3 mg/kg/day
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment:. No dosage adjustment.
- Hepatic Impairment: Severe impairment:15 mg once daily
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Headache/ Abdominal pain/ constipation/ nausea - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 1 to 3 hours
- Time to peak: 1.7 hours
- Duration: >1 day
- Half-life elimination: 1.5 ± 1 hour
- Important Notes:
- Use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) may increase risk of CDAD(Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea ) , especially in hospitalized patients
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Available data have not shown an increased risk of major birth defects/ not known if present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Lansoprazole may be confused with aripiprazole, dexlansoprazole
Prevacid may be confused with Pravachol, Prevpac, PriLOSEC, Prinivil
Read More
- Antimicrobial Stewardship School
- Sepsis Training Program
- Download Pocket Guide for Antibiotic Pharmacotherapy Book
- Microbiology Course | ABC Bacteria
- Infectious Disease E-News | FREE Subscription
- ABC antimicrobials | Know all about the Antimicrobials
- Road Map to Antimicrobial Stewardship Training Program
- Register Now in FADIC Clinical Research School
- FADIC Drug Information Fellowship
- Buy FADIC Toolkit for Writing Research to Write a Great Research Paper
- Read 10 Skills You Must Learn to Make a Research via Google Scholar in Arabic
- The FADIC Online Continuous Medical Improvement Programs & Mini-Courses.
- Check Now FADIC Book store and Buy books in different specialties.
- Watch Now FADIC TV to Keep your self Updated.
- FADIC Podcast focusing on varieties of pharmacist perspectives in different specialties.
- Subscribe Now in FADIC 2020 Daily News (FNN) and Keep Updated.
- Check Now about Coronavirus Resource Information Center.

 Log in
Log in Sign up
Sign up