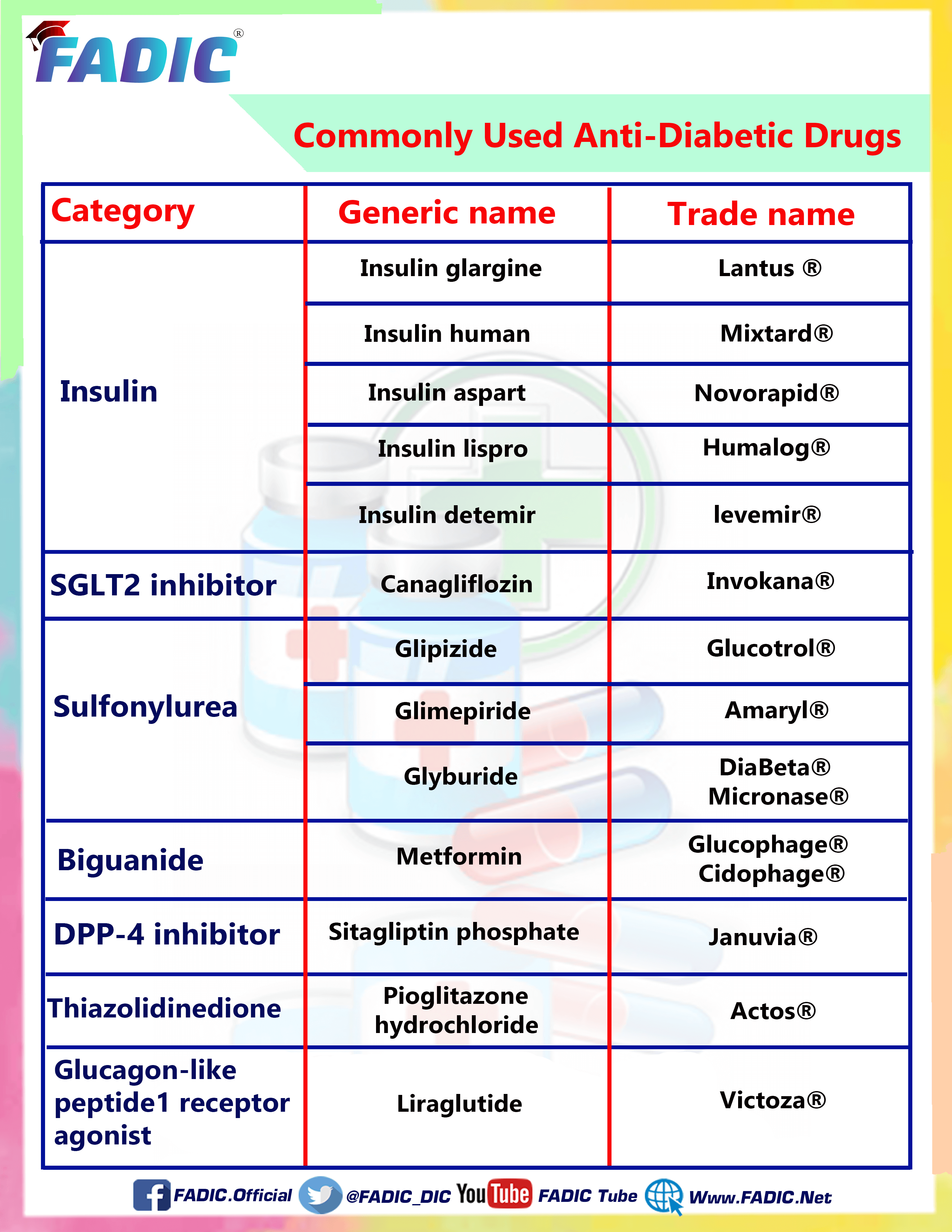
Top Anti-Diabetic Medications
The Most Famous eight drugs most Commonly used in the Treatment of Diabetic are:
1- Canagliflozin 💊
2- Glimepiride💊
3- GlipiZIDE 💊
4- Glyburide 💊
5- Metformin 💊
6-Liraglutide 💊
7- Pioglitazone 💊
8- Sitagliptin 💊
Canagliflozin
- Brand Names: Invokana
- Therapeutic Category: Antidiabetic Agent, SGLT2 Inhibitor
- Dosage Forms: Oral Tablet of Anti-Diabetic
- Use:
- Labeled Indications: Treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (noninsulin dependent, NIDDM) as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control
- Dosing: Diabetes mellitus, type 2: Oral: Initial: 100 mg once daily before the first meal of the day; may increase to 300 mg once daily
- Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing.
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment. eGFR 45 to <60 mL/minute/1.73 m2: Maximum dose: 100 mg once daily
- eGFR ≥30 to <45 mL/minute/1.73 m2: Use not recommended
- eGFR <30 mL/minute/1.73 m2: Use is contraindicated.
- Hepatic Impairment: Severe impairment: Use not recommended
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Increased serum potassium/ Genitourinary fungal infection/ Renal insufficiency/ Hypoglycemia - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: Within 24 hours
- Absorption: Not affected by food
- Time to peak, plasma: 1 to 2 hours
- Important Notes:
- Bone fractures: An increased incidence of bone fracture has been reported
- Genital mycotic infections: May increase the risk of genital mycotic infections (e.g., vulvovaginal mycotic infection, vulvovaginal candidiasis, vulvovaginitis)
- May cause symptomatic hypotension due to intravascular volume depletion, especially in patients with renal impairment
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Pregnancy category C/ not known if present in breast milk
Glimepiride
- Brand Names: Amaryl
- Therapeutic Category: Antidiabetic Agent, Sulfonylurea
- Dosage Forms: Oral Tablet of Anti-Diabetic
- Use:
- Labeled Indications: Diabetes mellitus, type 2, treatment (alternative agent): Adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Dosing : Initial: 1 to 2 mg once daily, administered with breakfast or the first main meal
- Geriatric: Oral: Initial: 1 mg once daily; dose titration and maintenance dosing should be conservative to avoid hypoglycemia.
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment. Consider alternative therapy if eGFR <15 mL/minute
- Hepatic Impairment: no dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Hypoglycemia/ Dizziness/ Nausea/ Flu-like symptoms - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 2 to 3 hours
- Half-life elimination: 5 to 9 hours
- Time to peak, plasma: 2 to 3 hours
- Important Notes:
- hypoglycemic drugs may be associated with an increased cardiovascular mortality
- All sulfonylurea drugs are capable of producing severe hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia is more likely to occur when caloric intake is deficient
- The FDA-approved product labelling for many medications containing a sulfonamide chemical group includes a broad contraindication in patients with a prior allergic reaction to sulfonamides.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Pregnancy category C/ not known if present in breast milk
- Medication safety issue:
- Glimepiride may be confused with glipiZIDE
- Amaryl may be confused with Altace, Amerge
GlipiZIDE
- Brand Names: Glucotrol
- Therapeutic Category: Antidiabetic Agent, Sulfonylurea
- Dosage Forms: Oral Tablet
- Use:
- Labeled Indications: Diabetes mellitus, type 2, treatment (alternative agent): Adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Dosing : Initial: 2.5 mg once daily administered 30 minutes before a meal (preferably before breakfast
- If adequate glycemic control is not obtained, may increase the dose in 2.5 to 5 mg increments no more frequently than every few days
- Maximum effective dose: 20 mg/day
- Geriatric: Initial: 2.5 mg once daily; consider titrating by 2.5 to 5 mg/day at 1- to 2-week intervals
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment. No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: Oral: Initial: 2.5 mg once daily; maintenance dosing should be conservative to avoid hypoglycemia
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Syncope/ Dizziness/ nervousness/ depression/ insomnia Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics: - Duration: 12 to 24 hours
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Half-life elimination: 2 to 5 hours
- Time to peak: 1 to 3 hours
- Important Notes:
- hypoglycemic drugs may be associated with an increased cardiovascular mortality
- All sulfonylurea drugs are capable of producing severe hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia is more likely to occur when caloric intake is deficient
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Pregnancy category C/ not detected in breast milk
- Medication safety issue:
- GlipiZIDE may be confused with glimepiride, glyBURIDE
- Glucotrol may be confused with Glucophage, Glucotrol XL, glyBURIDE, GlycoTrol (dietary supplement)
Glyburide
- Brand Names: Euglucon
- Therapeutic Category: Antidiabetic Agent, Sulfonylurea
- Dosage Forms: Oral Tablet of anti-Diabetic
- Use:
- Labeled Indications: Diabetes mellitus, type 2, treatment (alternative agent): Adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Off-Label: Gestational diabetes mellitus
- Dosing : Initial: 2.5 to 5 mg daily, administered with breakfast or the first main meal of the day.
- Maintenance: 1.25 to 20 mg daily given as single or divided doses.
- Maximum: 20 mg daily
- Geriatric: Glyburide is not a drug of choice for the elderly because of its association with severe hypoglycemia.
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment. No dosage adjustments
- Hepatic Impairment: no dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
heartburn/ Epigastric fullness/ nausea - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 15-60 minutes
- Half-life elimination: 10 hours
- Time to peak, plasma: 2 to 4 hours
- Important Notes:
- hypoglycemic drugs may be associated with an increased cardiovascular mortality
- All sulfonylurea drugs are capable of producing severe hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia is more likely to occur when caloric intake is deficient
- The FDA-approved product labelling for many medications containing a sulfonamide chemical group includes a broad contraindication in patients with a prior allergic reaction to sulfonamides.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Pregnancy category C/ may be present in breast milk
- Medication safety issue:
- GlyBURIDE may be confused with glipiZIDE, Glucotrol
- Diaβeta may be confused with Zebeta
- Micronase may be confused with Microzide
Metformin
- Brand Names: Glucophage
- Therapeutic Category: Anti-Diabetic Agent, Biguanide
- Dosage Forms: Oral (Tablet-Solution) of Anti-Diabetic
- Use:
- Labeled Indications: Diabetes mellitus, type 2: Management of type 2 diabetes mellitus when hyperglycemia cannot be managed with diet and exercise alone.
- Off-Label: Antipsychotic-induced weight gain/ Gestational diabetes mellitus/ Polycystic ovary syndrome/
- Dosing : Adult: Antipsychotic-induced weight gain, treatment (off-label use): 750 mg to 2 g daily in 2 to 3 divided doses
- Diabetes mellitus, type 2, treatment: Initial: 500 mg once or twice daily or 850 mg once daily/ Usual maintenance dosage: 1 g twice daily or 850 mg twice/ Maximum: 2.55 g/day
- Pediatric: Children ≥10 years and Adolescents: Oral: Initial: 500 to 1,000 mg once daily for 7 to 14 days; may increase the dose in 500 to 1,000 mg increments every 1 to 2 weeks as tolerated
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: eGFR 30 to 45: Use is not recommended for initiation of therapy
- Hepatic Impairment: avoid metformin since liver disease is considered a risk factor for developing lactic acidosis during metformin therapy.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Diarrhoea/ nausea and vomiting/ Chest discomfort, flushing, palpitations - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: Within days; maximum effects up to 2 weeks
- Half-life elimination: Plasma: 4 to 9 hours
- Metabolism: Not metabolised by the liver
- Important Notes:
- cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis have resulted in death, hypothermia, hypotension, and resistant bradyarrhythmias
- If metformin-associated lactic acidosis is suspected, immediately discontinue metformin
- Pregnancy & Lactation: crosses the placenta/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
- MetFORMIN may be confused with metronidazole
- Glucophage may be confused with Glucotrol, Glutofac
Liraglutide
- Brand Names: Victoza
- Therapeutic Category: Anti-Diabetic Agent, Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonist
- Dosage Forms: Solution Pen-injector, Subcutaneous
- Use:
- Labeled Indications: Chronic weight management: As an adjunct to a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity for chronic weight management in adult patients
- Diabetes mellitus, type 2: As an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Dosing: Chronic weight management: SubQ: Initial: 0.6 mg once daily for one week; increase by 0.6 mg daily at weekly intervals to a target dose of 3 mg once daily
- Diabetes mellitus, type 2 :SubQ: Initial: 0.6 mg once daily for one week; then increase to 1.2 mg once daily, may increase further to 1.8 mg once daily.
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment is necessary.
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustment is necessary
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Increased heart rate/ Headache/ Nausea/ diarrhea/ vomiting - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Bioavailability: SubQ: 55%
- Half-life, elimination: 13 hours
- Time to peak, plasma: 8 to 12 hours
- Important Notes:
- Liraglutide is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC and patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome types 2 (MEN 2).
- Counsel patients regarding the potential risk for MTC with the use of liraglutide and inform them of symptoms of thyroid tumours
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Use of liraglutide for chronic weight management is contraindicated in pregnant women/ not known if present in breast milk
Pioglitazone
- Brand Names: Actos
- Therapeutic Category: Anti-Diabetic Agent, Thiazolidinedione
- Dosage Forms: Oral Tablet of Anti-Diabetic
- Use:
- Labeled Indications: Diabetes mellitus, type 2: As an adjunct to diet and exercise, to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Dosing : Initial: 15 to 30 mg once daily
- the dosage increased in 15 mg increments up to a maximum of 45 mg once daily
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment is necessary.
- Hepatic Impairment: Hepatic impairment during therapy: If liver injury is suspected (e.g., fatigue, jaundice, dark urine): Interrupt treatment, measure serum liver tests
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Edema/ Hypoglycemia/ Cardiac failure/ Headache - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Peak effect: Glucose control: Several weeks
- Half-life elimination: Parent drug: 3 to 7 hours
- Time to peak: 2 hours; delayed with food
- Important Notes:
- Thiazolidinediones, including pioglitazone, can cause or exacerbate congestive heart failure (CHF) in some patients.
- Observe patients for signs and symptoms of heart failure (including excessive, rapid weight gain, dyspnea, and oedema). If these signs and symptoms develop, manage the heart failure according to the current standards of care.
- Pioglitazone is not recommended in patients with symptomatic heart failure
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Information related to the use of pioglitazone in pregnant women is limited/ not known if present in breast milk
- Medication Safety Issues
Actos may be confused with Actidose, Actonel.
Sitagliptin
- Brand Names: Januvia
- Therapeutic Category: Anti-Diabetic Agent, Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 (DPP-4) Inhibitor
- Dosage Forms: Oral Tablet
- Use:
- Labeled Indications: Diabetes mellitus, type 2: As an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Dosing: Diabetes mellitus, type 2: Oral: 100 mg once daily
- Concomitant use with insulin and insulin secretagogues (e.g., sulfonylureas): Reduced dose of insulin and insulin secretagogues needed.
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: eGFR ≥30 to <45 mL/minute/1.73 m2: 50 mg once daily
- eGFR <30 mL/minute/1.73 m2: 25 mg once daily
- Hepatic Impairment: no dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Diarrhea/ nausea/ Nasopharyngitis/ Hypoglycemia - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Bioavailability: 87%
- Half-life elimination: 12.4 hours
- Time to peak, plasma: 1 to 4 hours
- Important Notes:
- Arthralgia: Severe and disabling arthralgia reported with DPP-IV inhibitor use; onset may occur within one day to years after treatment initiation and may resolve with discontinuation of therapy.
- Discontinue use immediately if pancreatitis suspected and initiate appropriate management.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Pregnancy category B/ not known if present in breast milk
- Medication Safety Issues
Januvia is confused with Enjuvia, Janumet, and Jantoven.
SITagliptin confused with SAXagliptin, SUMAtriptan
Hashtags:
1. #AntiDiabetic
2. #DiabetesTreatment
3. #Medications
4. #BloodSugarControl
5. #DiabetesManagement
6. #Healthcare
7. #DiabetesAwareness
8. #InsulinTherapy
9. #DiabeticHealth
10. #Endocrinology
Read More:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship School
- Sepsis Training Program
- Download Pocket Guide for Antibiotic Pharmacotherapy Book
- Microbiology Course | ABC Bacteria
- Infectious Disease E-News | FREE Subscription
- ABC antimicrobials | Know all about the Antimicrobials
- Road Map to Antimicrobial Stewardship Training Program
- Register Now in FADIC Clinical Research School
- FADIC Drug Information Fellowship
- Buy FADIC Toolkit for Writing Research to Write a Great Research Paper
- Read 10 Skills You Must Learn to Do a Research via Google Scholar in Arabic
- The FADIC Online Continuous Medical Improvement Programs & Mini-Courses.
- Check Now FADIC Book store and Buy books in different specialities.
- Watch Now FADIC TV to Keep yourself Updated.
- FADIC Podcast focuses on varieties of pharmacist perspectives in different specialities.
- Subscribe Now to FADIC 2020 Daily News (FNN) and Keep Updated.
- Check Now about Coronavirus Resource Information Center.

 Log in
Log in Sign up
Sign up