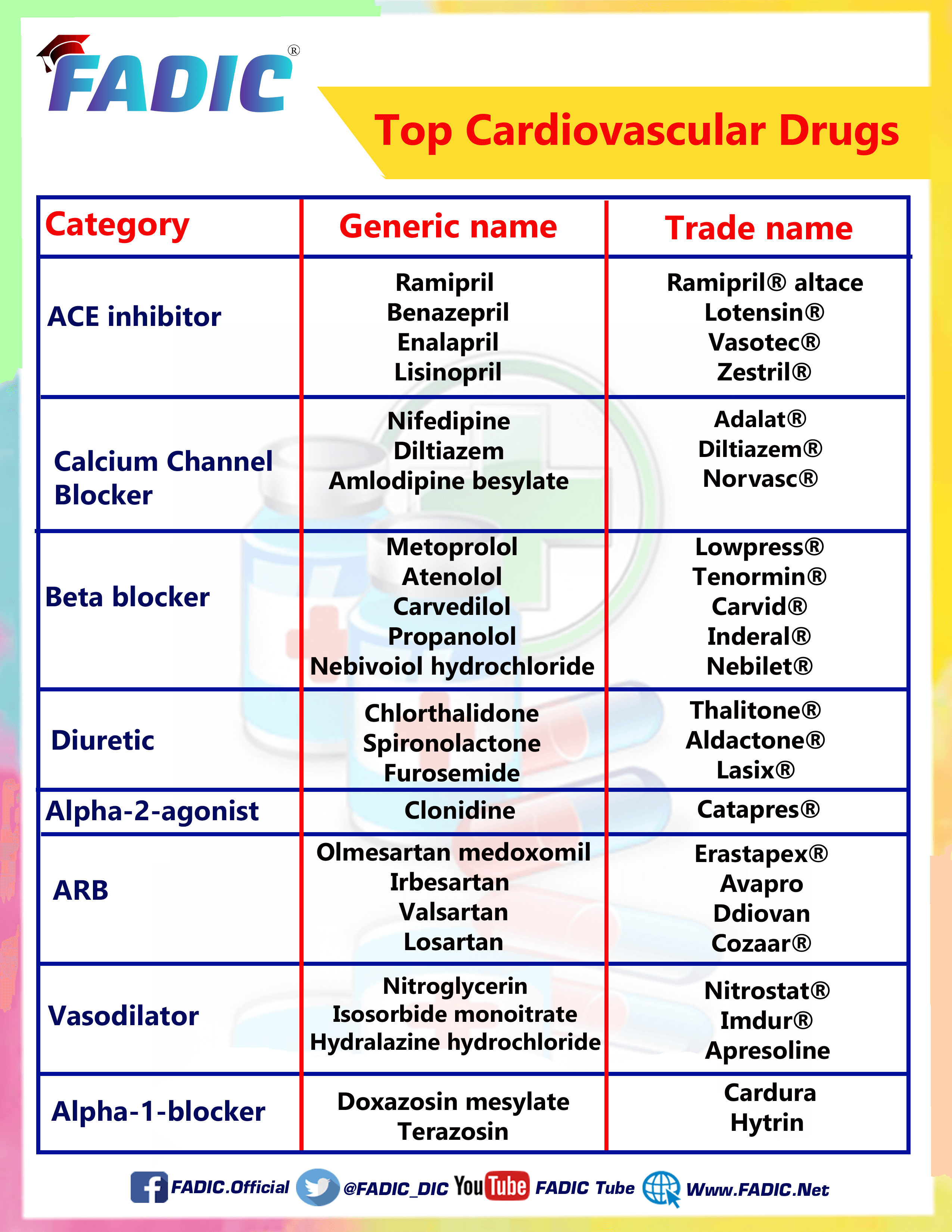
The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs commonly used are:
1- Amlodipine 💊
2- Atenolol 💊
3- Benazepril 💊
4- Carvedilol 💊
5- Chlorthalidone💊
6- Clonidine 💊
7- Diltiazem 💊
8- Doxazosin 💊
9- Enalapril 💊
10- Furosemide 💊
11- Hydralazine 💊
12- Isosorbide Dinitrate 💊
13- Lisinopril 💊
14- Metoprolol 💊
15-Nebivolol 💊
16- Nifedipine 💊
17- Nitroglycerin 💊
18-Propranolol 💊
19- Ramipril 💊
20- Spironolactone 💊
21- Terazosin 💊
Amlodipine
- Brand Names: Norvasc
- It is one of The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: calcium channel blocker
- Dosage Forms: oral tablet
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Chronic stable angina/ Hypertension/ Stable coronary artery disease with ongoing ischemic symptoms/ Vasospastic angina
- Off-Label Indications: Raynaud phenomenon
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult Oral: Initial: 2.5 to 5 mg once daily; titrate every 1 to 2 weeks as needed based on patient response; maximum: 10 mg/day
- Geriatric: Elderly patients show decreased clearance of amlodipine.
- Oral: Initial: 2.5 mg once daily
- Pediatric: Oral: 2.5 to 5 mg once daily
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: Oral: Initial: 2.5 mg once daily; titrate slowly in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Peripheral oedema/ Pulmonary oedema - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 24 to 48 hours
- Time to peak: Oral: 6 to 12 hours
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Half-life elimination: 30 to 50 hours
- Important Notes:
- Symptomatic hypotension can occur
- The most common side effect is peripheral oedema, which occurs within 2 to 3 weeks of starting therapy.
- Use amlodipine with extreme caution in patients with severe aortic stenosis; it may reduce coronary perfusion resulting in ischemia.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ Present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
AmLODIPine may be confused with aMILoride.
Norvasc may be confused with Navane, Norvir, or Vascor.
ِAtenolol
- Brand Names: Tenormin
- It is one of The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: Beta-Blocker
- Dosage Forms: oral (Capsule/ tablet)/ IV solution
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Acute myocardial infarction/ Angina pectoris caused by coronary atherosclerosis/ Hypertension
- Off-Label Indications: Atrial fibrillation / Ventricular arrhythmias
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult Initial: 50 mg once daily; may increase to 100 mg once daily. Some patients may require 200 mg once daily.
- Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing
- Pediatric: Hypertension: Oral: Children and Adolescents: Initial: 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/dose either once daily or divided into doses twice daily
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: CrCl 15 to 35 mL/minute/1.73 m2: Maximum dose: 50 mg daily
- CrCl <15 mL/minute/1.73 m2: Maximum dose: 25 mg daily
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Hypotension/ cardiac failure/ Fatigue/ depression - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: Oral: ≤1 hour
- Time to peak: Oral: 2 to 4 hours
- Metabolism: Limited hepatic
- Half-life elimination: 6 to 7 hours, prolonged with renal impairment
- Important Notes:
- Following abrupt discontinuation of therapy with beta-blockers, exacerbations of angina pectoris and myocardial infarction (MI) have occurred
- When discontinuing long-term administration, gradually reduce the dose over 1 to 2 weeks, monitor the patient, and advise the patient to limit physical activity to a minimum.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor D/ Present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Atenolol may be confused with albuterol, Altenol, timolol, Tylenol
Tenormin may be confused with Imuran, Norpramin, thiamine, TrovanMetoprolol succinate may be confused with metoprolol tartrate
Benazepril
- Brand Names: Lotensin
- It is one of The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor
- Dosage Forms: oral (Tablet)
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Hypertension
- Off-Label Indications: Heart failure/ Stable coronary artery disease
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: Oral: Initial: 5 to 10 mg once daily; titrate as needed based on patient response up to 40 mg daily in 1 or 2 divided doses
- Geriatric: Consider lower initial doses
- Pediatric : Children ≥6 years and Adolescents: Oral: Initial: 0.2 mg/kg once daily, maintenance: 0.1 to 0.6 mg/kg once daily
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment. CrCl <30 mL/minute Initial: 5 mg once daily; maximum dose: 40 mg/day
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Hypotension/ Headache/ dizziness - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 1-2 hours
- Metabolism: hepatic to its active metabolite, benazeprilat
- Half-life elimination: Benazeprilat: Effective: 10 to 11 hours
- Time to peak, serum: Parent drug: 0.5 to 1 hour
- Active metabolite (benazeprilat): 1 to 2 hours
- Important Notes:
- When pregnancy is detected, discontinue as soon as possible. As it can cause injury and death to the developing fetus
- ACE inhibitors may be preferred agents in elderly patients with CHF and diabetes mellitus.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor D/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Benazepril may be confused with Benadryl.
Lotensin may be confused with Lioresal, lorcaserin, and lovastatin.
Carvedilol
- Brand Names: Coreg/ Carvid
- Therapeutic Category: Beta-Blocker With Alpha-Blocking Activity
- Dosage Forms: oral (Capsule/ tablet)
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF)/ Hypertension/ Left ventricular dysfunction following MI
- Off-Label Indications: Acute MI/ Atrial fibrillation/ Chronic stable angina/ Ventricular arrhythmias
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: hypertension: initial: 6.25 mg twice daily; titrate dose every 1 to 2 weeks as needed based on patient response up to a maximum of 25 mg twice daily
- HFrEF: 3.125 mg twice daily for two weeks; if this dose is tolerated, may increase to 6.25 mg twice daily
- Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: Severe impairment: Use is contraindicated.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Hypotension/ orthostatic hypotension / Fatigue/ dizziness - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: Alpha-blockade: Within 30 minutes; Beta-blockade: Within 1 hour
- Time to peak: 1 to 2 hours
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Half-life elimination: 7 to 10 hours
- Important Notes:
- Should be taken with food to minimise the risk of orthostatic hypotension
- Treatment of anaphylaxis (e.g., epinephrine) in patients taking beta-blockers may be ineffective or promote undesirable effects.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor c/ Present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Carvedilol may be confused with atenolol, captopril, carbidopa, carteolol
Coreg may be confused with Corgard, Cortef, Cozaar
Chlorthalidone
- Brand Names: Apo-Chlorthalidone
- Therapeutic Category: Diuretic
- Dosage Forms: oral (tablet)
- Labeled Indications: Edema/ Hypertension
- Off-label indication: Calcium nephrolithiasis
- Dosing:
- Edema: Oral: Initial: 50 to 100 mg once daily or 100 mg on alternate days; maximum: 200 mg/day
- Hypertension: Oral: Initial: 12.5 to 25 mg once daily; titrate as needed based on patient response to 50 mg once daily
- Renal Impairment: no dosage adjustments
- Hepatic Impairment: no dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Orthostatic hypotension, vasculitis, Dizziness, headache
Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 2.6 hours
- Peak effect: 2 to 6 hours
- Half-life elimination: Single dose: 40 hours
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Important Notes:
- Hypokalemia, hypochloremic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia, and hyponatremia may occur.
- Hypersensitivity reactions may occur. The risk increases in patients with a history of allergy or bronchial asthma.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor B/ present in breast milk
Clonidine
- Brand Names: Catapres/ Kapvay
- It is one of The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: Alpha2-Adrenergic Agonist
- Dosage Forms: Solution, Epidural/ Tablet( Oral, Extended release)
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) (extended-release tablet)/ Hypertension (immediate-release tablet) / Pain management (epidural)
- Off-Label Indications: Clozapine-induced sialorrhea/ Conduct disorder with or without (ADHD)
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: Initial dose: 0.1 mg twice daily; maximum amount: 2.4 mg/day
- Pediatric : hypertension: Children ≥12 years: Immediate release: Initial: 0.2 mg/day in 2 divided doses , maximum: 2.4 mg/day
- ADHD: Children ≤45 kg: Initial: 0.05 mg at bedtime; sequentially increase every 3 to 7 days by 0.05 mg increments twice daily, maximum daily dose: 0.2 mg/day
- When discontinuing therapy, taper gradually over 1 to 2 weeks.
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: Dosage adjustment according to the degree of renal impairment
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Drowsiness/ headache/ fatigue/ dizziness - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: Antihypertensive effect: Oral: Immediate release: 0.5 to 1 hour/ ADHD: Oral: Extended-release (Kapvay): Onset of action: 1 to 2 weeks
- Half-life elimination: Adults:12 to 16 hours
- Time to peak, serum: Oral: Immediate release: 1 to 3 hours; Extended-release (Kapvay): 7 to 8 hours
- Important Notes:
- Epidural clonidine is not recommended for obstetrical, postpartum, or perioperative pain management because of The risk of hemodynamic instability, especially hypotension and bradycardia.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor c/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
CloNIDine may be confused with Clomid, clomiPHENE, clonazePAM, cloZAPine, KlonoPIN, and quiNIDine.
Catapres may be confused with Cataflam, Combipres
Diltiazem
- Brand Names: Diltiazem
- It is one of The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: calcium channel blocker
- Dosage Forms: oral (tablet/capsule)/ solution IV
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Management of hypertension/ management of chronic stable angina
- Off-Label Indications: Anal fissures/ Atrial fibrillation/ Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy/ Raynaud phenomenon
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult : Initial: 60 to 120 mg twice daily; dose adjustment may be made after 14 days; usual dose range: 120 to 180 mg twice daily
- Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing
- Pediatric: Oral: Initial: 1.5 to 2 mg/kg/day in 3 to 4 divided doses
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: no dosage adjustments.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Edema/ Headache/ Dizziness - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 30 to 60 minutes
- Bioavailability: Oral: 40%
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Half-life elimination: 3 to 4.5 hours
- Time to peak: 2 to 4 hours
- Important Notes:
- May cause first-, second-, and third-degree AV block or sinus bradycardia
- Transient dermatologic reactions have been observed with the use
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ Present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Cardizem may be confused with Cardene, Cardene SR, Cardizem CD, Cardizem SR, and cortisone.
Cartia XT may be confused with Procardia XL.
DilTIAZem may be confused with Calan, diazePAM, Dilantin
Tiazac may be confused with Tigan, Tiazac XC [CAN], Ziac
Doxazosin
- Brand Names: Cardura
- It is one of The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: Alpha 1 Blocker
- Dosage Forms: oral (tablet)
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Benign prostatic hyperplasia/ Hypertension
- Off-Label Indications: Pediatric hypertension/ Ureteral calculi
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult : Initial: 1 mg once daily; may titrate (by doubling the daily dose [e.g., to 2 mg, then 4 mg, then 8 mg]) at 1- to 2-week intervals up to 8 mg once daily
- Geriatric: In the management of hypertension, consider a lower initial dose
- Pediatric: Initial: 1 mg once daily; maximum: 4 mg/day
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: Severe impairment: Use is not recommended.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Dizziness /malaise /fatigue / headache - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Time to peak, serum: 2 to 3 hours
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Half-life elimination: 22 hours
- Time to peak: 2 to 3 hours
- Important Notes:
- May cause CNS depression, which may impair physical or mental abilities
- Intraoperative floppy iris syndrome has been observed in cataract surgery patients who were on or were previously treated with alpha1-blockers
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Doxazosin crosses the placenta / Present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Doxazosin may be confused with doxapram, doxepin, DOXOrubicin
Cardura may be confused with Cardene, Cordarone, Cordran, Coumadin, K-Dur, Ridaura
Enalapril
- Brand Names: Vasotec
- It is one of The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor
- Dosage Forms: oral (Tablet/ solution)
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction/Heart Failure/ Hypertension
- Off-Label Indications: Non–ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome/ Stable coronary artery disease
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult and geriatric: Heart failure: Oral: Initial: 2.5 mg twice daily (maximum: 40 mg/day); titrate slowly at 1- to 2-week intervals. Target dose: 10 to 20 mg twice daily
- Hypertension: Oral: Initial: 5 mg once daily; titrate at 1- to 2-week intervals up to 40 mg daily in 1 or 2 divided doses
- Pediatric : hypertension: Oral: Initial: 0.08 mg/kg once daily
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: CrCl ≤30 mL/minute: Initial: 2.5 mg once daily; titrate upward (maximum: 40 mg/day)
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Increased serum creatinine/ Hypotension/ Dizziness - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 1 hour
- Peak effect: 4 to 6 hours
- Duration: 12 to 24 hours
- Half-life elimination: Enalapril :Adults: Healthy: 2 hours; CHF: 3.4 to 5.8 hours
Enalaprilat: adults: 35 hours
- Time to peak, serum: Oral: Enalapril: 0.5 to 1.5 hours, Enalaprilat (active metabolite): 3 to 4.5 hours
- Important Notes:
- When pregnancy is detected, discontinue as soon as possible. As it can cause injury and death to the developing fetus
- ACE inhibitors may be preferred agents in elderly patients with CHF and diabetes mellitus.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor D/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Enalapril may be confused with Anafranil, Elavil, Eldepryl, or ramipril.
Furosemide
- Brand Names: Lasix
- It is one of The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: Diuretic
- Dosage Forms: oral (tablet/ solution)/ Injection
- Labeled Indications: Management of oedema associated with heart failure/ Hypertension
- Dosing:
- Oral: Initial: 20 to 80 mg/dose; if the response is not adequate, may repeat the same dose or increase dose in increments of 20 to 40 mg/dose at intervals of 6 to 8 hours
- Heart failure: Initial: 20 to 40 mg once or twice daily; maximum 600 mg/day
- IM, IV: Initial: 20 to 40 mg/dose
- Hypertension: Usual dosage range: 20 to 80 mg/day in 2 divided doses
- Renal Impairment: Acute renal failure: Doses up to 1 to 3 g daily may be necessary to initiate the desired response
- Hepatic Impairment: Monitor effects, particularly with high doses.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
orthostatic hypotension/ Dizziness/ headache/ Abdominal cramps - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: Oral, sublingual (SL): 30 to 60 minutes/ IM: 30 minutes
- Bioavailability: Oral tablet: 47% to 64%
- Peak effect: Oral/ IV: 0.5 hours
- Half-life elimination: Normal renal function: 0.5 to 2 hours
- Important Notes:
- Furosemide is a potent diuretic that, if given excessively, can lead to a profound diuresis with water and electrolyte depletion.
- Nephrotoxicity: Monitor fluid status and renal function in an attempt to prevent oliguria
- Sulfonamide (“sulfa”) allergy: contraindicated in patients with a prior allergic reaction to sulfonamides.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Furosemide may be confused with famotidine, finasteride, fluconazole, FLUoxetine, fosinopril, loperamide, torsemide
Lasix may be confused with Lanoxin, Lidex, Lomotil, Lovenox, and Luvox.
Hydralazine
- Brand Names: Apresoline
- Therapeutic Category: Vasodilator
- Dosage Forms: oral (tablet)/ Injection (solution)
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Hypertension
- Off-Label Indications: Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF)/ Hypertensive emergency in pregnancy or postpartum
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult : Oral: Initial: 25 to 50 mg 3 or 4 times daily in combination with isosorbide dinitrate 3 or 4 times daily.
- Hypertensive emergency in pregnancy: IM, IV: Initial: 5 or 10 mg; repeat with 5 to 10 mg doses every 20 minutes if blood pressure continues to exceed
- Pediatric: Hypertension, chronic: Oral: Initial: 0.75 mg/kg/day in 2 to 4 divided doses
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: no dosage adjustments.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Angina pectoris/ Anxiety/ depression/ dizziness - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: IV: 10 to 80 minutes
- Bioavailability: Increased with food
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Half-life elimination: 3 to 7 hours
- Important Notes:
- Drug-induced lupus-like syndrome: This may cause a drug-induced lupus-like syndrome, including glomerulonephritis, especially in patients receiving higher doses.
- Hydralazine has been associated with peripheral neuritis.
- Use is contraindicated in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ Present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
HydrALAZINE may be confused with hydrOXYzine.
Isosorbide Dinitrate
- Brand Names: Dilatrate-SR/ Isordil Titradose
- Therapeutic Category: Vasodilator
- Dosage Forms: oral (tablet/ capsule)
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Prevention of angina pectoris
- Off-Label Indications: Achalasia/ Heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: Achalasia (off-label use): Sublingual: Immediate release: 5 mg administered 10 to 15 minutes before meals
- Angina pectoris (prevention): Immediate release: Initial: 5 to 20 mg 2 to 3 times daily
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: no dosage adjustments.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, Dizziness - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: Sublingual tablet: 2 to 5 minutes
- Bioavailability: Highly variable (10% to 90%)
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Half-life elimination: Parent drug: 1 hour
- Important Notes:
- Severe hypotension can occur
- Nitrates may precipitate or aggravate increased intracranial pressure and subsequently may worsen clinical outcomes in patients with neurologic injury
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ Not known if present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Isordil may be confused with Inderal, Isuprel, and Plendil.
Lisinopril
- Brand Names: Zestril
- Therapeutic Category: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor
- Dosage Forms: oral (Tablet/ solution)
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction(HFrEF /ST-elevation myocardial infarction/ Hypertension
- Off-Label Indications: Non–ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome/ Stable coronary artery disease/ Proteinuric chronic kidney disease
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult : (HFrEF): Oral: Initial: 2.5 to 5 mg once daily; target dose40 mg once daily
- Hypertension: Oral: Initial: 5 to 10 mg once daily
- Could be combined with another antihypertensive drug
- Pediatric : Children ≥6 years: Oral: Initial: 0.07 to 0.1 mg/kg once daily (maximum initial dose: 5 mg/day); increase dose at 1- to 2-week intervals; maximum: 0.6 mg/kg/day or 40 mg/day
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: (HFrEF): CrCl 10 to 30 mL/minute: Initial: 2.5 mg once daily (maximum: 40 mg/day)
- Hypertension: CrCl 10 to 30 mL/minute: Initial: 5 mg once daily (maximum: 40 mg/day)
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Hypotension/ Dizziness/ Increased serum creatinine - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 1 hour
- Peak effect: 6 hours
- Duration: 24 hours
- Half-life elimination: 12 hours
- Time to peak, serum: 7 hours
- Important Notes:
- When pregnancy is detected, discontinue as soon as possible. As it can cause injury and death to the developing fetus
- ACE inhibitors may be preferred agents in elderly patients with CHF and diabetes mellitus.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor D/ present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Lisinopril may be confused with fosinopril, Lioresal, Lipitor, RisperDAL
Zestril may be confused with Desyrel, Restoril, Vistaril, Zegerid, Zerit, Zetia, Zostrix, ZyPREXA
Metoprolol
- Brand Names: Lopressor/ Betaloc
- Therapeutic Category: Beta-Blocker
- Dosage Forms: oral (Capsule/ tablet)/ IV solution
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Angina / Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF)/ Hypertension/ Myocardial infarction
- Off-Label Indications: Atrial fibrillation / Migraine prophylaxis/ Ventricular arrhythmias
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult Oral: Initial: 50 mg twice daily; may increase the dose at weekly intervals to the desired effect, usual dosage range: 50 to 200 mg twice daily, maximum dose: 400 mg/day
- Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing
- Pediatric: Children ≥1 year of age and Adolescents ≤17 years of age (off-label population): Initial: 0.5 to 1 mg/kg/dose (maximum initial dose: 25 mg/dose) twice daily
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Hypotension, bradycardia, dizziness - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: Within 1 hour
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Bioavailability: Oral: 40% to 50%
- Half-life elimination: 3 to 4 hours
- Important Notes:
- Following abrupt discontinuation of therapy with beta-blockers, exacerbations of angina pectoris and myocardial infarction (MI) have occurred
- When discontinuing long-term administration, gradually reduce the dose over 1 to 2 weeks and monitor the patient
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ Present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Lopressor may be confused with Lyrica.
Metoprolol may be confused with metaproterenol, metoclopramide, metOLazone, and miSOPROStol.
Metoprolol succinate may be confused with metoprolol tartrate.
Nebivolol
- Brand Names: Bystolic
- It is one of The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: Beta-Blocker
- Dosage Forms: oral ( tablet)
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Hypertension
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: Hypertension Oral: Initial: 5 mg once daily; titrate as needed at 2-week intervals based on patient response to a maximum dose of 40 mg once daily
- Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: CrCl <30 mL/minute: Initial: 2.5 mg once daily; if the initial response is inadequate, it may increase cautiously.
- Hepatic Impairment: Severe impairment: Use is contraindicated.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Headache/ dizziness/ fatigue - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Bioavailability: 12% (extensive metabolizers); 96% (poor metabolizers)
- Time to peak: 1.5 to 4 hours
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Half-life elimination: 12 hours (extensive metabolisers) or 19 hours (poor metabolites)
- Important Notes:
- In general, patients with bronchospastic disease should not receive beta-blockers
- Treatment of anaphylaxis (e.g., epinephrine) in patients taking beta-blockers may be ineffective or promote undesirable effects.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ not known if is present in breast milk.
Nifedipine
- Brand Names: Adalat
- It is one of The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: calcium channel blocker
- Dosage Forms: oral (tablet/capsule)
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Angina/ Hypertension
- Off-Label Indications: Achalasia/ High altitude pulmonary edema/ Hypertensive emergency in pregnancy/ Preterm labor/ Raynaud phenomenon
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult : angina: Initial: 10 mg 3 times daily; usual dose: 10 to 20 mg 3 times daily
- Hypertension emergency in pregnancy: Oral: Immediate release: 10 mg; may repeat with a 20 mg dose in 20 minutes if needed.
- Geriatric: Refer to adult dosing
- Pediatric: 5 mg/kg/dose (maximum: 20 mg/dose) every 8 hours
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: no dosage adjustments.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Flushing/ Dizziness/ headache/ Heartburn / nausea - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 20 minutes
- Bioavailability: Capsule: 40% to 77%
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Half-life elimination: 2 to 5 hours
- Important Notes:
- Symptomatic hypotension with or without syncope can rarely occur
- Reflex tachycardia may occur, resulting in angina
- The most common side effect is peripheral oedema.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ Present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
NIFEdipine may be confused with niCARdipine, niMODipine, nisoldipine
Procardia XL may be confused with Cartia XT.
Nitroglycerin
- Brand Names: Nitrostat/ Nitronal
- It is one of The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: Vasodilator
- Dosage Forms: oral (tablet/ capsule)/ Aerosol Solution, Translingual/ Ointment/ Transdermal patch/ solution (IV, Translingual)
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Treatment or prevention of angina pectoris/ Treatment of moderate-to-severe pain associated with chronic anal fissure
- Off-Label Indications: Esophageal spastic disorders/ Gastroesophageal variceal haemorrhage/ Uterine relaxation
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult: Oral: Initial: 2.5 to 6.5 mg 3 to 4 times daily; may titrate up to 26 mg 4 times daily
- Topical 2% ointment: 1/2” upon rising and 1/2” 6 hours later; if necessary, the dose may be doubled to 1” and subsequently doubled again to 2” if the response is inadequate
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: no dosage adjustments.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Headache/ Hypotension/ Dizziness/ syncope - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: Sublingual tablet: 1 to 3 minutes
- Peak effect: Sublingual tablet: 5 minutes
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Half-life elimination: 1 to 4 minutes
- Important Notes:
- Headache: Dose-related headaches may occur, especially during initial dosing.
- Hypotension/bradycardia: Severe hypotension and shock may occur (even with small doses)
- Increased intracranial pressure: Nitroglycerin may precipitate or aggravate increased intracranial pressure
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ Not known if present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Nitroglycerin may be confused with nitrofurantoin, nitroprusside
Nitro-Bid may be confused with Macrobid
Nitroderm may be confused with NicoDerm
Nitrol may be confused with Nizoral
Nitrostat may be confused with Nilstat, nystatin
Propranolol
- Brand Names: Inderal
- Therapeutic Category: Beta-Blocker
- Dosage Forms: oral (Capsule/solution/tablet)/ IV solution
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Cardiac arrhythmias/ Essential tremor/ Hypertension/ Migraine headache prophylaxis/ Pheochromocytoma/ Stable angina
- Off-Label Indications: Performance anxiety/ Supraventricular tachycardia/ Thyroid storm/ antipsychotic-induced Akathisia
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult : Initial: 10 mg twice daily or 10 mg 3 times daily; adjust dose based on response and tolerability up to 120 mg/day
- Hypertension: 40 mg twice daily/ maximum dose: 640 mg/day
- Geriatric: Consider lower initial doses
- Pediatric: hypertension:oral: Immediate-release formulations: Initial: 1 to 2 mg/kg/day divided in 2 to 3 doses/day; titrate dose to effect; maximum dose: 4 mg/kg/day up to 640 mg/day
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Cold extremities/ Sleep disorder/ agitation/ fatigue - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 1-2 hours
- Metabolism: hepatically metabolised to active and inactive compounds
- Bioavailability: 25% reaches systemic circulation
- Half-life elimination: 3 to 6 hours
- Time to peak, serum: 1 to 4 hours
- Important Notes:
- Following abrupt discontinuation of therapy with beta-blockers, exacerbations of angina pectoris and myocardial infarction (MI) have occurred
- When discontinuing long-term administration, gradually reduce the dose over 1 to 2 weeks and monitor the patient
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ Present in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Propranolol may be confused with prasugrel, Pravachol, Propulsid
Inderal may be confused with Adderall, Enduron, Imdur, Imuran, Inderide, Isordil, Toradol
Ramipril
- Brand Names: Altace, Ramipril
- It is one of The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor
- Dosage Forms: oral (Capsule)
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Heart failure post-myocardial infarction/ Hypertension/ Reduction in risk of MI, stroke, and death from cardiovascular causes
- Off-Label Indications: Stable coronary artery disease/ Heart failure with a reduced ejection fraction
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult and Geriatric: Heart failure: Initial: 2.5 mg twice daily for one week, then titrate every three weeks upward to a target dose of 5 mg twice daily.
- Hypertension:: Initial: 2.5 mg once daily; titrate after 2 to 4 weeks up to 20 mg daily
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment:CrCl <40 mL/minute: Administer 25% of normal dose. Hepatic Impairment: No dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Hypotension/ Increased cough/ Angina pectoris - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 1-2 hours
- Metabolism: Hepatic to the active form, ramiprilat
- Bioavailability: Ramipril: 28%; Ramiprilat: 44%
- Half-life elimination: Ramiprilat: Effective: 13-17 hours
- Time to peak, serum: Ramipril: ~1 hour; Ramiprilat: 2-4 hours
- Important Notes:
- When pregnancy is detected, discontinue ramipril as soon as possible. As it can cause injury and death to the developing fetus
- ACE inhibitors may be preferred agents in elderly patients with CHF and diabetes mellitus.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor D/ not detected in breast milk
- Drug safety issue:
Ramipril may be confused with enalapril, Monopril, Amaryl
Altace may be confused with Altace HCT, alteplase, Amaryl, Amerge, Artane
Spironolactone
- Brand Names: Aldactone
- It is one of The Most Common Heart Disease Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: Diuretic
- Dosage Forms: oral (tablet/ suspension)
- Labeled Indications: Management of oedema for cirrhosis of the liver
Heart failure/ Hypertension
Off-label indication: Acne vulgaris (females)/ Hirsutism
- Dosing:
Adult: Edema: Tablet: Oral: Initial: 100 mg daily in single or divided doses; dosage range: 25 to 200 mg daily in single or divided doses.
Hypertension: Oral: Initial: Tablet: 25 to 50 mg daily in 1 or 2 divided doses; may titrate every two weeks as needed based on patient response up to 100 mg daily
- Renal Impairment: Treating Heart failure: eGFR 30 to 50 mL/minute/1.73 m2: Initial: 25 mg every other day.
- Hepatic Impairment: no dosage adjustments
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Gynecomastia/ Vasculitis/ confusion/ dizziness/ drowsiness/ headache - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Duration: Tablet: 2 to 3 days
- Bioavailability: High-fat/calorie meal increased the bioavailability of spironolactone by 90%
- Time to peak, serum: Tablet: 2.6 to 4.3 hours
- Half-life elimination: Tablet: Spironolactone: 1.4 hours
- Important Notes:
- Gynecomastia: May occur; risk increases based on dose, and onset is variable (after 1 to 2 months to over a year of therapy); usually reversible following treatment discontinuation.
- Hyperkalemia may occur; the risk of hyperkalemia is increased with renal impairment
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk Factor C/ The active metabolite of spironolactone (canrenone) is present in breast milk.
- Drug safety issue:
Aldactone may be confused with Aldactazide.
Terazosin
- Brand Names: Hytrin
- It is one of The Most Common Heart diseases Drugs
- Therapeutic Category: Alpha 1 Blocker
- Dosage Forms: oral (Capsule)
- Use: Heart Disease Drugs
- Labeled Indications: Benign prostatic hyperplasia/ Hypertension
- Off-Label Indications: Pediatric hypertension/ Ureteral calculi
- Dosing:
- Dosing Adult : Oral: Initial: 1 mg at bedtime; most patients require 10 mg once daily; if no response after 4 to 6 weeks of 10 mg/day, may increase to 20 mg/day
- Geriatric: In the management of hypertension, consider a lower initial dose
- Pediatric: Initial: 1 mg once daily, typically administered at bedtime; slowly increase the dose to achieve desired blood pressure as tolerated; maximum daily dose: 20 mg/day
- Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: No dosage adjustment
- Hepatic Impairment: Severe impairment: Use is not recommended.
- Adverse Drug Interaction:
Dizziness /myasthenia /Peripheral oedema / orthostatic hypotension - Pharmacodynamics/Kinetics:
- Onset of action: 15 minutes
- Time to peak, serum: 2 to 3 hours
- Metabolism: Hepatic
- Half-life elimination: 12 hours
- Time to peak: 1 hour
- Important Notes:
- May cause CNS depression, which may impair physical or mental abilities
- Intraoperative floppy iris syndrome has been observed in cataract surgery patients who were on or were previously treated with alpha1-blockers
- Inappropriate medication in patients 65 years and older due to its high risk of orthostatic hypotension.
- Pregnancy & Lactation: Risk factor C / not known if present in breast milk
Read More:
- Antimicrobial Stewardship School
- Sepsis Training Program
- Download Pocket Guide for Antibiotic Pharmacotherapy Book
- Microbiology Course | ABC Bacteria
- Infectious Disease E-News | FREE Subscription
- ABC antimicrobials | Know all about the Antimicrobials
- Road Map to Antimicrobial Stewardship Training Program
- Register Now in FADIC Clinical Research School
- FADIC Drug Information Fellowship
- Buy FADIC Toolkit for Writing Research to Write a Great Research Paper
- Read 10 Skills You Must Learn to Do Research via Google Scholar in Arabic
- The FADIC Online Continuous Medical Improvement Programs & Mini-Courses.
- Check Now FADIC Book store and Buy books in different specialities.
- Watch Now FADIC TV to Keep Yourself Updated.
- FADIC Podcast focuses on varieties of pharmacist perspectives in different specialities.
- Subscribe Now to FADIC 2020 Daily News (FNN) and Keep Updated.
- Check Now about Coronavirus Resource Information Center.
- Read now The Big 6 Heart Medications

 Log in
Log in Sign up
Sign up